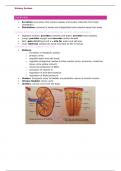
Respiration
STEPS OF RESPIRATION
1. Ventilation
Exchange of air between the atmosphere and alveoli
2. Gas exchange (external)
Between alveoli air and blood
3. Gas transport
4. Gas exchange (internal)
Between blood in capillaries and cells in tissue
5. Cellular respiration
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Primary Function:
To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the air
1. Bring oxygen (O2) into the body.
2. Rid the body of carbon dioxide (CO2).
3. Regulate blood pH.
Respiratory gases exchange between animals/humans and the environment is very important because:
All cells require energy to survive, grow and reproduce.
Cells rely on aerobic metabolism.
Without oxygen, cellular processes cannot continue.
COMPONENTS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The respiratory system is divided into two parts:
1. The upper respiratory tract
2. The lower respiratory tract
, Image from: 1https://microbiologynotes.com/respiration-and-respiratory-organs/
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT
1. Nose(external)
2. Sinuses – frontal and sphenoid bones
3. Nasal cavity (internal)
4. Mouth
5. Throat (Pharynx)
6. Epiglottis
7. Glottis
8. Part of the Trachea that has the larynx (structure associated with sound production)
Larynx serves to:
o Maintain and open airway.
o Route food and air into appropriate channels
o Assist in the production of sound.
Larynx contains the epiglottis and the vocal cords.
The epiglottis = cartilage located at the opening of the Larynx
The vocal cord consists of connective tissue that surrounds the opening of the airway (Glottis).
The vocal cords stretch across the tracheal opening and vibrate as air passes through it when you start
talking.
STEPS OF RESPIRATION
1. Ventilation
Exchange of air between the atmosphere and alveoli
2. Gas exchange (external)
Between alveoli air and blood
3. Gas transport
4. Gas exchange (internal)
Between blood in capillaries and cells in tissue
5. Cellular respiration
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Primary Function:
To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the air
1. Bring oxygen (O2) into the body.
2. Rid the body of carbon dioxide (CO2).
3. Regulate blood pH.
Respiratory gases exchange between animals/humans and the environment is very important because:
All cells require energy to survive, grow and reproduce.
Cells rely on aerobic metabolism.
Without oxygen, cellular processes cannot continue.
COMPONENTS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The respiratory system is divided into two parts:
1. The upper respiratory tract
2. The lower respiratory tract
, Image from: 1https://microbiologynotes.com/respiration-and-respiratory-organs/
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT
1. Nose(external)
2. Sinuses – frontal and sphenoid bones
3. Nasal cavity (internal)
4. Mouth
5. Throat (Pharynx)
6. Epiglottis
7. Glottis
8. Part of the Trachea that has the larynx (structure associated with sound production)
Larynx serves to:
o Maintain and open airway.
o Route food and air into appropriate channels
o Assist in the production of sound.
Larynx contains the epiglottis and the vocal cords.
The epiglottis = cartilage located at the opening of the Larynx
The vocal cord consists of connective tissue that surrounds the opening of the airway (Glottis).
The vocal cords stretch across the tracheal opening and vibrate as air passes through it when you start
talking.