. Put whole number/fraction in front of formula
. Big number = multiplies whole compound
. Small number = multiplies specific atom
State symbols in equation:
. Acid = aqueous (aq)
. Pure metal = solid (s)
. Liquid = l
. Gas = g
, 1. Principles of Chemistry
States of Matter (1.1 - 1.3)
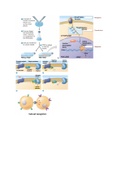
Describe arrangement, Molecules close together in a regular arrangement
motion and energy of Molecules vibrate about a fixed point
particles in solids Low energy
(1.1-1.2)
Describe arrangement, Molecules close together in an irregular arrangement
motion and energy of Molecules move around each other in random directions at slow speeds
particles in liquids Greater energy than solids
(1.1-1.2)
Describe arrangement, Molecules far apart in a random arrangement
motion and energy of Molecules move in random directions at high speeds
particles in gases Highest energy
(1.1-1.2)
Evaporation/Boiling Liquid → Gas (at boiling point)
Condensation Gas → Liquid (at boiling point)
Sublimation Solid → Gas
Resublimation Gas → Solid
Freeze Liquid → Solid (chemically bonded at melting point)
Melt Solid → Liquid (chemically broken at melting point)
Effects of Interconversions Solids → Liquids → Gases:
b/w States of Matter Increased K.E → Increased movement → Further apart + Random Arrangement
Diffusion (1.3) Random movement of particles from area of high conc → area of low conc
Cannot occur in solids as particles cannot move freely
Diffusion Examples Potassium manganate diffuses in water from area of high to low concentration
Adding more water to purple solution → particles evenly spread out and mix with
water molecules so purple solution becomes diluted
Bromine gas diffuses through air in jar when glass plate removed
Diffusion of Ammonia and Hydrogen Chloride
Concentrated ammonia solution diffuses faster so is closer to hydrochloric acid
b/c particles are lighter
Diffuse at different speeds b/c masses different + particles randomly collide
,Solubility (1.4 - 1.7C)
Solute Solid substance being dissolved into liquid solvent to form a solution
Solvent Liquid substance that dissolves solid solute
Solution Mixture formed when solute dissolves in solvent
Solubility Maximum mass (in grams) of a solute which can be dissolved in 100g of solvent
Saturated Solution Maximum amount of solute in a solvent that can be held at a particular
volume and temperature
Solubility Practical . Make saturated solution by using pipette to add excess ammonium chloride to
10cm3 of water in boiling tube (ammonium chloride will sink to bottom)
. Stir solution w/ glass rod to dissolve ammonium chloride, heat to 25°C using
Solubility Curve bunsen burner and confirm temp w/ thermometer
. Weigh empty evaporating basin on balance
. Filter solution into evaporating basin + reweigh
. Gently heat solution until all water evaporates (pure ammonium chloride forms)
and reweigh
- don’t heat to high b/c ammonium chloride will escape as gas and alter mass of
solid in basin so solubility value will be inaccurate
. Repeat practical at different temperatures (35°C, 45°C etc.)
. Solid mass = (Evaporating basin + pure solid) - (Evaporating basin)
. Water removed mass = (basin + saturated solution) - (basin + solid)
. Draw graphs w/ different LOBF to compare solubility
. Solubility = mass of solid/mass of water x 100
. Independent Variable (X-axis) = Temperature in °C
. Dependent Variable (Y-axis) = Solubility in g/100g water
. Control variables = Volume of water + Volume of solutions
Exam Q Tips:
B/c of solubility formula: . Half solute → Half temperature
. Half water → Double temperature
Soluble Substance can be dissolved
Insoluble Substance cannot be dissolved
Miscible Substance can be mixed
Immiscible Substance cannot be mixed
, Elements, Compounds, Mixtures (1.8 - 1.10)
Element Only same type of atom that is chemically bonded
Compound Two or more different atoms that are chemically bonded
Mixture Two or more different atoms that are not chemically bonded
Have a melting/boiling range
Pure Substances Single element or compound not mixed w/ another substance
(1.9) Confirmed by fixed melting/boiling point
E.g. Water Boiling Point = 100°C & Water Melting Point = 0°C
Separating Mixtures (1.11 - 1.13)
Simple Distillation Separation of mixture of miscible liquids or solvent from solution
E.g. Ethanol from Water
. Turn on water tap for bottom and top of condenser so it completely fills up and
keeps surrounding glass sleeve cold
. Add anti-bumping granules to solution in beaker, to preventing bubbles forming
. Solution heated in condensing tube using bunsen burner until it evaporates (l → g)
. Liquid vapour cools/condenses in tube (gas → liquid) and is it rises up flask
. Liquid is collected in separate beaker (distillate)
Fractional Distillation Separation of mixture of miscible liquids
E.g. Crude Oil
. Mixture heated using bunsen burner until it boils and gas is at bottom of column
. Fractions at top = higher temperature and bottom = lower temperature
. Fractions condense at different heights b/c they have different boiling points
. Liquid is collected in separate test tube
Fraction w/ higher boiling point = removed from bottom of fractionating column
Fraction w/ lower boiling point = removed from top of fractionating column
Filtration Separation of insoluble solid from a liquid or liquid from an insoluble solid
E.g. Sand from Water
. Pour mixture into funnel with filter paper to separate insoluble solid from liquid
. Solid particles are too big to fit through holes in filter paper
. Collect filtrate (liquid) in separate beaker underneath funnel as solid residue left
Crystallisation Separation of soluble solids from solution
E.g. Salt Crystals from Salt Water
. Heat solution in evaporating dish using bunsen burner to evaporate some water
. Until crystals form on glass rod (showing hot saturated solution has formed)
. Leave solution to cool and crystallise
. Separate crystals from solvent by filtration
. Dry crystals in a drying oven or desiccator (contains chemicals that remove water)