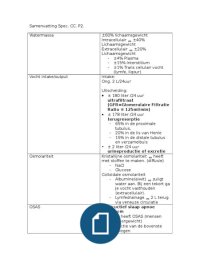
UA BSC 315 Exam 1 Study Guide With
Complete Solutions
Heredity - ANSWER The process of how genes transmit traits from parents to offspring
Genes - ANSWER Units of heredity encoded by DNA sequences that underlie the
formation of every heritable trait in every organism
Alleles - ANSWER Alternative forms of a single gene
Phenotype - ANSWER Physical characteristics of an organism
Genotype - ANSWER An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
Monohybrid Cross - ANSWER Mating pure-breeding parental plants antagonistic for a
single trait
Gametes - ANSWER Specialized haploid cells that carry genes between generations
(egg/sperm)
Segregation - ANSWER Separation of alleles so that each gamete receives only one
copy of each gene
Product rule - ANSWER Probability of two independent events occurring together is the
product of their individual probabilities
Sum rule - ANSWER Probability of either of two mutually exclusive events occurring is
the sum of their individual probabilities
Testcross - ANSWER Cross between an organism with an unknown genotype and an
organism with a recessive phenotype
Dihybrid crosses produce _______________ types and ________________ types - ANSWER
parental; recombinant
What is the formula for the possible number of gamete genotypes from a hybrid -
ANSWER 2^n
where n = number of heterozygous traits
Law of Segregation - ANSWER Mendelian law stating that two alleles for each trait
separate during meiosis
Law of Independent Assortment - ANSWER Mendel's second law, stating that allele pairs
separate from one another during gamete formation
, What type of trait follows a horizontal pattern of inheritance? - ANSWER A rare
autosomal recessive trait
What type of trait follows a vertical pattern of inheritance? - ANSWER A rare dominant
trait
Pleiotropy - ANSWER One gene may contribute to several characteristics
Complete dominance - ANSWER Hybrid resembles one of the two parents
Incomplete dominance - ANSWER Hybrid resembles neither parent (blend)
Codominance - ANSWER Hybrid shows traits from both parents
Allele frequency - ANSWER Percentage of the total number of gene copies for one allele
in a population
Wild-type - ANSWER Most common allel
Mutant allele - ANSWER Rare allele
Monomorphic gene - ANSWER Only one common allele
Polymorphic gene - ANSWER More than one common allele
What is the offspring ratio for a recessive lethal allele? - ANSWER 2:1
Single traits arising from interaction of multiple genes are __________________ - ANSWER
multifactorial
What is the ratio of F2 phenotypes from dihybrid crosses? - ANSWER 9:3:3:1
Two genes involved
Complementary gene action - ANSWER When two true breeding organisms for the same
phenotype yield an F1 generation that is all of a different phenotype.
What is the F2 ratio of progeny for complementary gene action? - ANSWER 9:7 in favor
of the non-parental phenotype
Epistasis - ANSWER An allele at one locus masks the effects of an allele at another locus
The gene that masks is ____________ to the other gene - ANSWER epistatic
The gene that is masked is ______________ to the other gene - ANSWER hypostatic
Complete Solutions
Heredity - ANSWER The process of how genes transmit traits from parents to offspring
Genes - ANSWER Units of heredity encoded by DNA sequences that underlie the
formation of every heritable trait in every organism
Alleles - ANSWER Alternative forms of a single gene
Phenotype - ANSWER Physical characteristics of an organism
Genotype - ANSWER An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
Monohybrid Cross - ANSWER Mating pure-breeding parental plants antagonistic for a
single trait
Gametes - ANSWER Specialized haploid cells that carry genes between generations
(egg/sperm)
Segregation - ANSWER Separation of alleles so that each gamete receives only one
copy of each gene
Product rule - ANSWER Probability of two independent events occurring together is the
product of their individual probabilities
Sum rule - ANSWER Probability of either of two mutually exclusive events occurring is
the sum of their individual probabilities
Testcross - ANSWER Cross between an organism with an unknown genotype and an
organism with a recessive phenotype
Dihybrid crosses produce _______________ types and ________________ types - ANSWER
parental; recombinant
What is the formula for the possible number of gamete genotypes from a hybrid -
ANSWER 2^n
where n = number of heterozygous traits
Law of Segregation - ANSWER Mendelian law stating that two alleles for each trait
separate during meiosis
Law of Independent Assortment - ANSWER Mendel's second law, stating that allele pairs
separate from one another during gamete formation
, What type of trait follows a horizontal pattern of inheritance? - ANSWER A rare
autosomal recessive trait
What type of trait follows a vertical pattern of inheritance? - ANSWER A rare dominant
trait
Pleiotropy - ANSWER One gene may contribute to several characteristics
Complete dominance - ANSWER Hybrid resembles one of the two parents
Incomplete dominance - ANSWER Hybrid resembles neither parent (blend)
Codominance - ANSWER Hybrid shows traits from both parents
Allele frequency - ANSWER Percentage of the total number of gene copies for one allele
in a population
Wild-type - ANSWER Most common allel
Mutant allele - ANSWER Rare allele
Monomorphic gene - ANSWER Only one common allele
Polymorphic gene - ANSWER More than one common allele
What is the offspring ratio for a recessive lethal allele? - ANSWER 2:1
Single traits arising from interaction of multiple genes are __________________ - ANSWER
multifactorial
What is the ratio of F2 phenotypes from dihybrid crosses? - ANSWER 9:3:3:1
Two genes involved
Complementary gene action - ANSWER When two true breeding organisms for the same
phenotype yield an F1 generation that is all of a different phenotype.
What is the F2 ratio of progeny for complementary gene action? - ANSWER 9:7 in favor
of the non-parental phenotype
Epistasis - ANSWER An allele at one locus masks the effects of an allele at another locus
The gene that masks is ____________ to the other gene - ANSWER epistatic
The gene that is masked is ______________ to the other gene - ANSWER hypostatic