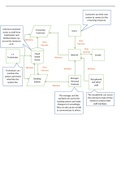
Socialism Introduction
Context & strands of socialism
Socialism as an ideology develops in the 19th century amid the industrialisation of
Europe.
Fundamentalist Socialists are united in the belief that capitalism and socialism are
incompatible – there are too many contradictions in capitalism and it will always exploit
However, they differ in their ways of getting rid of capitalism
o Revolutionary socialism (Marx & Engels, Lenin, Luxemburg) – belief in the
need for a revolution to get rid of capitalism, it won't go in its own time.
Marx (Marxism) believes all history is based on class – appealed
to young Russian peasants as a way out of their backwardness
as he believed there will ultimately be a socialist revolution and
the state will wither away, ending up with a utopian classless
society.
Lenin (Marxism-Leninism) has a particular interpretation of
Marxism – says you can cut out the capitalist phase and go
almost straight from a feudalistic system to a socialist system
with dedicated revolutionaries
Luxemburg, a Marxist by definition, believed that a revolution
was only made possible by developing class consciousness, and
it had to come from the workers
o Democratic socialism (Webb)
Webb is a member of the Fabian society, which advocated for
socialism via democratic means. She believed in the 'Inevitability
of gradualism', arguing that socialism will inevitably happen as
countries are democratising and over time people will vote for
socialist parties which will then bring about a socialist society.
Social Democracy (Crossland, Attlee), a separate strand of socialism to fundamentalist
socialism
o Belief that you can create the ends of socialism through a capitalist
framework (humanising capitalism) via things such as Keynesianism and
nationalisation. Society is infinitely more complex than it was in
fundamental socialist times and therefore socialist ends such as equality
have to be created through capitalism.
Third Way Socialism (Giddens, Blair, Clinton (a bit)), develops in the 1980s and 1990s.
o Argues for a neo-liberal view of the economy with a social-democratic view
of society. Much more comfortable with people getting rich and being pro-
business as they can use tax receipts for good public services. Alteration of
Clause IV, which therefore decommitted Labour from nationalisation of all
industry. Critics argue that Third Way Socialism is not Socialism and is
instead a type of neo-liberal proto-Thatcherism
Human Nature
Takes a positive view within reason – many believe that in some way human nature has
been corrupted by capitalism.
The State
For the most part, socialists believe in a big state, as a big state is needed to create the
huge change.
Marx believes this is the role of the state – to bring about change and then wither away.
The Economy
, Large differences exist between the views of different socialist thinkers on the economy
– revolutionary thinkers see capitalism as inconsistent with socialism, whereas Third
Way socialists and Social Democrats believe capitalism can be tamed
Revolutionary Socialism
As industrialisation occurs, there becomes a greater awareness of the problems of capitalism –
poverty, inequality, etc. Socialism develops because there is a perceived belief that liberalism
doesn't adequately deal with the problems thrown up by the industrial revolution. Class is
important.
Key Concepts
Social class - "The history of all hitherto existing society is this history of class struggle"
o Marx' entire analogy of society is through the lens of social class – there is
oppressed and there is oppressor.
The Bourgeoisie and the Proletariat
o Two classes – the bourgeoisie (the ruling class, the people who own the
means production) and the proletariat (the working class, the people who
sell their labour to get by)
The Hegelian Dialectic
o There is an original idea (a thesis), which is then challenged by an antithesis
and they come together in a higher form of understanding called a
synthesis.
The Marxist Dialectic
o Marx adapts Hegel's idea through the focus of class. Different classes come
about through time and society goes through a series of changes.
o Feudalism (absolute monarchy/aristocracy ruling class) -> Bourgeois
revolution -> Capitalism (democracy, middle class ruling class) -> Socialist
revolution (due to wealth disparity and the proletariat developing class
consciousness) -> Socialism (dictatorship of the proletariat) -> Transition to
Communism -> Communism (the state withers away, society is equal, each
from their ability, each to their need)
Historical determinism
o Idea that things are predetermined in society – there are social, structural,
and economic forces that predetermine events.
Historical materialism
o The idea that material conditions are what drive history – not individuals or
ideas, but economics and peoples' conditions.
False consciousness
o What sustains capitalism – that the proletariat are deceived and are
unaware that they are being exploited by the bourgeoisie.
o Religion & materialism are part of this.
Class consciousness
o Under capitalism, class consciousness is when the proletariat become aware
of their class status, power, and position, and then rise up.
Internationalism
Context & strands of socialism
Socialism as an ideology develops in the 19th century amid the industrialisation of
Europe.
Fundamentalist Socialists are united in the belief that capitalism and socialism are
incompatible – there are too many contradictions in capitalism and it will always exploit
However, they differ in their ways of getting rid of capitalism
o Revolutionary socialism (Marx & Engels, Lenin, Luxemburg) – belief in the
need for a revolution to get rid of capitalism, it won't go in its own time.
Marx (Marxism) believes all history is based on class – appealed
to young Russian peasants as a way out of their backwardness
as he believed there will ultimately be a socialist revolution and
the state will wither away, ending up with a utopian classless
society.
Lenin (Marxism-Leninism) has a particular interpretation of
Marxism – says you can cut out the capitalist phase and go
almost straight from a feudalistic system to a socialist system
with dedicated revolutionaries
Luxemburg, a Marxist by definition, believed that a revolution
was only made possible by developing class consciousness, and
it had to come from the workers
o Democratic socialism (Webb)
Webb is a member of the Fabian society, which advocated for
socialism via democratic means. She believed in the 'Inevitability
of gradualism', arguing that socialism will inevitably happen as
countries are democratising and over time people will vote for
socialist parties which will then bring about a socialist society.
Social Democracy (Crossland, Attlee), a separate strand of socialism to fundamentalist
socialism
o Belief that you can create the ends of socialism through a capitalist
framework (humanising capitalism) via things such as Keynesianism and
nationalisation. Society is infinitely more complex than it was in
fundamental socialist times and therefore socialist ends such as equality
have to be created through capitalism.
Third Way Socialism (Giddens, Blair, Clinton (a bit)), develops in the 1980s and 1990s.
o Argues for a neo-liberal view of the economy with a social-democratic view
of society. Much more comfortable with people getting rich and being pro-
business as they can use tax receipts for good public services. Alteration of
Clause IV, which therefore decommitted Labour from nationalisation of all
industry. Critics argue that Third Way Socialism is not Socialism and is
instead a type of neo-liberal proto-Thatcherism
Human Nature
Takes a positive view within reason – many believe that in some way human nature has
been corrupted by capitalism.
The State
For the most part, socialists believe in a big state, as a big state is needed to create the
huge change.
Marx believes this is the role of the state – to bring about change and then wither away.
The Economy
, Large differences exist between the views of different socialist thinkers on the economy
– revolutionary thinkers see capitalism as inconsistent with socialism, whereas Third
Way socialists and Social Democrats believe capitalism can be tamed
Revolutionary Socialism
As industrialisation occurs, there becomes a greater awareness of the problems of capitalism –
poverty, inequality, etc. Socialism develops because there is a perceived belief that liberalism
doesn't adequately deal with the problems thrown up by the industrial revolution. Class is
important.
Key Concepts
Social class - "The history of all hitherto existing society is this history of class struggle"
o Marx' entire analogy of society is through the lens of social class – there is
oppressed and there is oppressor.
The Bourgeoisie and the Proletariat
o Two classes – the bourgeoisie (the ruling class, the people who own the
means production) and the proletariat (the working class, the people who
sell their labour to get by)
The Hegelian Dialectic
o There is an original idea (a thesis), which is then challenged by an antithesis
and they come together in a higher form of understanding called a
synthesis.
The Marxist Dialectic
o Marx adapts Hegel's idea through the focus of class. Different classes come
about through time and society goes through a series of changes.
o Feudalism (absolute monarchy/aristocracy ruling class) -> Bourgeois
revolution -> Capitalism (democracy, middle class ruling class) -> Socialist
revolution (due to wealth disparity and the proletariat developing class
consciousness) -> Socialism (dictatorship of the proletariat) -> Transition to
Communism -> Communism (the state withers away, society is equal, each
from their ability, each to their need)
Historical determinism
o Idea that things are predetermined in society – there are social, structural,
and economic forces that predetermine events.
Historical materialism
o The idea that material conditions are what drive history – not individuals or
ideas, but economics and peoples' conditions.
False consciousness
o What sustains capitalism – that the proletariat are deceived and are
unaware that they are being exploited by the bourgeoisie.
o Religion & materialism are part of this.
Class consciousness
o Under capitalism, class consciousness is when the proletariat become aware
of their class status, power, and position, and then rise up.
Internationalism