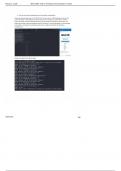
Earth’s Resources:
What we Where it comes from
need
Oxygen Air
Water Rain
Food Plants and animals
Clothes Fibres made from chemicals in oil (e.g. nylon,
polyesters) or from natural fibres from plants (e.g.
cotton) or animals (e.g. wool)
Shelter/ Building materials include; stone, sand, bricks made
buildings from clay, cement made from limestone and clay,
timber and trees.
Warmth Burning fuels
Electricity Generated using fuels
Fuel for Burning fuels
transport
Medicines Mainly made from chemicals found in oil or plants
Fertilisers From plant and animal waste or made from nitrogen
in the air, water, natural gas and minerals from the
ground
Metals Made from ores in the ground
Polymers Mainly made from chemical found in oil
(plastics)
A finite resource is a resource that cannot be replaced once it has been
used.
A renewable resource is a that we can replace once we have used it.
Sustainable development is using resources to meet the needs of
people today without preventing people in the future from meeting
theirs.
Life cycle assessment:
A life cycle assessment is carried out to assess the impact of a product
on the environment throughout its life.
This includes:
o Extraction of raw materials
o It’s manufacture
o It’s uses
o It’s disposal
o Use of sustainability of raw materials (including packaging)
o Use of energy at all stages
o Use of water at all stages
, o Production and disposals of waste products (including pollutants)
at all stages
o Transportation and distribution at all stages
Types of Water:
Pure water – only contains water molecules, has nothing dissolved and
no microbes present.
Fresh water – water found in lakes, rivers, ice caps, glaciers,
underground rocks and streams. Has a low level of dissolved
substances and some microbes present
Sea water – water in seas and oceans, high levels of dissolved
substances and does contain microbes.
Potable water – water that is safe to drink, low levels of dissolved
substances, no or very low levels or microbes.
Ground water – water found in porous rocks and underground streams,
has low levels of dissolved substances and some microbes.
Wastewater – used water from homes, industry and agriculture,
microbes present and high levels of dissolved salt.
Filtration is used to remove solids, sterilisation to kill microbes. In
countries with little fresh water they use distillation and reverse
osmosis.
In some parts of the world Saudi Arabia, there is little fresh water but
there is lots of sea water. Potable water can be made from sea water
by desalination. Two methods of doing this are distillation and reverse
osmosis. Desalination uses vast amounts of energy.
o Distillation – Sea water is heated so that it boils. The water
molecules are turned to steam leaving behind the dissolved
substances. The water vapour is then cooled and condensed.
o Reverse osmosis – sea water is passed through a semipermeable
membrane using pressure. The water molecules pass through the
membrane but many of the dissolved substances cannot. This is
the opposite of normal osmosis where water would move in the
opposite direction. \
Wastewater treatment
Stage What happens
Screening and grit Removes large solids from the wastewater
removal
Primary Organic waste sinks to bottom as sludge.
sedimentation Remaining water taken from the top.
tanks
Aeration Good bacteria kill harmful bacteria in aeration
tanks where air is pumped through.
Final settling tanks Good bacteria sink to bottom in sludge.
Sludge treatment In the absence of air bacteria produce methane
from sludge
Burners Methane burned for heat and electricity