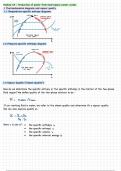
1 Thermodynamics diagrams and vapour quality
1.1 Temperature-specific entropy diagrams
CRITICAL POINT
⑧
TA
HERED VanSt
SAT
,
HDu
vau 47406
Y
ne 354
Lives OF CONST
Pressure
E
TWO-PHASe Region
"WET STEAM"
⑳
S
1.2 Pressure-specific enthalpy diagram
CRITICAL POIN
SathizeAnA
·
Pr YOU "
When
curve 270
naue ·
t TwoPhaseReaa LINE
S
OF
Temp
CONST
D
S
1.3 Vapour Quality (“Steam Quality”)
How do we determine the specific entropy or the specific enthalpy in the interior of the two-phase
fluid region? We define quality of the two-phase mixture to be -
X = Munrour /Moth
If our working fluid is water, we refer to the steam quality and otherwise it’s a vapour quality
We can also express quality as
X =
y -
9t
Yg- Ye
Here y is one of : • the specific enthalpy h
• the specific entropy S
• the specific volume V
• the specific internal energy U
, Example : From the steam tables we find -
Sy(60°) = 0 .
5725 v/(kgK)
Ta
Sy(60 % ) = 8 .
2570 vJ/gk)
Joi
2
Sg(502) Sg(oc)S
Now X =
S -
35 = 0 .
706 Or 70 6 %
.
Sy- Sg
As we know X =
h -
he =>
h =
hg + X (hy hs) -
hy-hy
FromThe Stratables hy(doc) = 167 57.
vT/g
hg (10°) = 2574 3 .
5/kg
WeFind h = 1866 7 /kg ·
2 Steam Turbines
Here we are thinking about turbines in which the working fluid expands from saturated vapour or
superheated vapour to either wet-steam (two-phase fluid) or superheated vapour.
Pi , hi ,Ti , si v@
Recall the Isentropic efficiency of a turbine -
is vin It = hi-hza
hi -
has
② VPz , ha , Ta ,
Worked example
Steam enters a well-designed turbine at 3 MPa and 400^C, and leaves at 50 kPa and 100^C. If the
power output of the turbine is 2 MW, then determine:
(a) The specific enthalpies of the inlet and outlet if the turbine is Isentropic
Goo
%
At 3MPa , TsaT
°
= 233 90 .
C so FLUID At C is superheated Steam.
From the superheated table at 3 MPa : Th
↓ (boo" 3 MPa) ,
= 3230 9 .
vJIng ① 3 MPa
s(booc 3 MPa) ,
= 6 9212
.
Jing ⑧
50 Pa
2a
2s
*
S