Respiratory system
Thoracic wall
- Rib cage
- 12 pairs of ribs
- Sternum & xyphoid
- Costal cartilages
- 12 thoracic vertebrae
- Intercostal muscles
binding the ribs to one
another
- Diaphragm
- Protects contents of thoracic activity
- Provides mechanical and muscular function of breathing
Pulmonary respiration
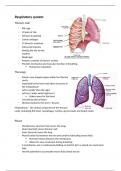
The lungs
- Paired, cone shaped organs within the thoracic
cavity
- Separated by the heart and other structures in
the mediastinum
- Left is smaller than the right
- Left has 2 lobes whilst right has 3
Makes space for the heart
- Covered by pleural layers
- Divisions between the loves = fissures
Mediastinum – the central component of the thoracic
cavity containing the heart, oesophagus, traches, great vessels and lymph nodes
Pleura
- Membranous structure that covers the lungs
- Outer (parietal) covers thoracic wall
- Inner (visceral) covers the lung
- Pleural cavity lies between the two and contains lubricating serous fluid.
Prevents friction between the membranes
Allows for easy movement during breathing
- 2 membranes, one is continuously folding on itself to form a closed sac round each
lobe
- Has the potential to accumulate excess fluid, blood and air
, Pneumothorax
- The accumulation of air in the pleural space.
- Air fills thoracic cavity, less space for lung
(life threatening)
Pleural effusion
- Excessive build-up of fluid in the pleural
space.
- Fluid moves to the lowest point
- Restricts lung expansion so respirations
increase
- A tube may be inserted to allow drainage
Respiratory tract
Sinuses
- Hollow spaces in the head’s bones
- Connected to the nose through small
openings
- Help to regulate temp / humidity of the
air breathed in
- Lightens bone structure of head
- Resonates voice
Nose
- Preferred entrance of outside air into resp. system
- 3 scroll like bones (turbinates / conchae)
- Hairs that line the walls are part of the air-cleaning system (vibrissae)
Mouth
- Air can also enter here
- Air enters when nasal passages may be temporarily obstructed
Adenoids
- Lymph tissue at the top of the throat
- Can be removed if they are interfering with breathing
- Carries fluids around the body with nodes and connecting vessels (lymph
system)
Thoracic wall
- Rib cage
- 12 pairs of ribs
- Sternum & xyphoid
- Costal cartilages
- 12 thoracic vertebrae
- Intercostal muscles
binding the ribs to one
another
- Diaphragm
- Protects contents of thoracic activity
- Provides mechanical and muscular function of breathing
Pulmonary respiration
The lungs
- Paired, cone shaped organs within the thoracic
cavity
- Separated by the heart and other structures in
the mediastinum
- Left is smaller than the right
- Left has 2 lobes whilst right has 3
Makes space for the heart
- Covered by pleural layers
- Divisions between the loves = fissures
Mediastinum – the central component of the thoracic
cavity containing the heart, oesophagus, traches, great vessels and lymph nodes
Pleura
- Membranous structure that covers the lungs
- Outer (parietal) covers thoracic wall
- Inner (visceral) covers the lung
- Pleural cavity lies between the two and contains lubricating serous fluid.
Prevents friction between the membranes
Allows for easy movement during breathing
- 2 membranes, one is continuously folding on itself to form a closed sac round each
lobe
- Has the potential to accumulate excess fluid, blood and air
, Pneumothorax
- The accumulation of air in the pleural space.
- Air fills thoracic cavity, less space for lung
(life threatening)
Pleural effusion
- Excessive build-up of fluid in the pleural
space.
- Fluid moves to the lowest point
- Restricts lung expansion so respirations
increase
- A tube may be inserted to allow drainage
Respiratory tract
Sinuses
- Hollow spaces in the head’s bones
- Connected to the nose through small
openings
- Help to regulate temp / humidity of the
air breathed in
- Lightens bone structure of head
- Resonates voice
Nose
- Preferred entrance of outside air into resp. system
- 3 scroll like bones (turbinates / conchae)
- Hairs that line the walls are part of the air-cleaning system (vibrissae)
Mouth
- Air can also enter here
- Air enters when nasal passages may be temporarily obstructed
Adenoids
- Lymph tissue at the top of the throat
- Can be removed if they are interfering with breathing
- Carries fluids around the body with nodes and connecting vessels (lymph
system)