• The vertebrate limb shows enormous morphological variety
o Similar basic structure between species but limbs look different
o
• The chicken embryo, in particular its developing limbs, can be easily manipulated
o A hole is cut in the top of the egg
o The embryo sits on top of the yolk
o Limb buds can then be manipulated
o Egg is sealed up again
o
• Malformation of the limbs are amongst the most common birth defects
o So common because limbs aren’t necessary for viable life
o Knowledge of developmental processes provides a framework for
understanding anatomical malformations in the adult
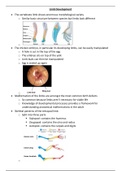
• Skeletal patterns of the tetrapod limb
o Split into three parts
▪ Stylopod- contains the humerus
▪ Zeugopod- contains the ulna and radius
▪ Autopod- contains the carpals and digits
o
, • Axis orientation of the developing limb bud
o In developmental body axis, the arm is held at 90 degrees to the body with
palm facing towards the ground
o
• The vertebrate limbs develop from the limb bud
o Limbs elongate along the proximal distal axis
o Parts between the digits are eliminated by apoptosis
o Outgrowth is controlled by the apical ectodermal ridge (AER)
▪ AER is made up of growing mesodermal cells
• The AER specifies the proximo-distal axis acting on the underlying mesenchyme
o The AER is found anteriorly
o If AER is removed limb developments stops
▪ The stage the limb stops growing depends when the AER is removed
• The later the AER is removed, the more the limb will develop
o If an extra AER is added, the wing is duplicated
o If leg mesenchyme is introduced, the wing will develop some leg characteristics
o If non-limb mesenchyme is introduced the AER regresses and limb
development ceases
o If AER is replaced by an FGF bead, a normal wing is formed
▪ This showed that FGF8 was expressed in the AER
o