AfraTafreeh.com
Last edited: 6/23/2023
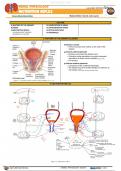
MICTURITION REFLEX
Renal | Micturition Reflex Medical Editor: Gerard Jude Loyola
OUTLINE
I) ANATOMY OF THE URINARY III) COMPOSITION OF URINE
BLADDER IV) SUPPLEMENTARY IMAGE
II) MICTURITION REFLEX V) REVIEW QUESTIONS
(A) DURING AN EMPTY BLADDER VI) REFERENCES
(B) DURING A FULL BLADDER
I) ANATOMY OF THE URINARY BLADDER
Detrusor muscle
o A thick muscular layer makes up the walls of the
bladder
Internal urethral sphincter
o Muscles surrounding the bladder neck
o Contracts during ejaculation to prevent retrograde
ejaculation of semen into the bladder [Moore, 2018]
o For females
External urethral sphincter
o Component of the urogenital diaphragm
o The striated muscle is located distally and inferiorly to
the bladder neck [Sam, Jiang & LaGrange, 2020]
Figure 1. Coronal section of the urinary bladder [Moore, 2018].
II) MICTURITION REFLEX
AfraTafreeh.com
Figure 2. Micturition reflex.
MICTURITION REFLEX RENAL PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 6
, (A) DURING AN EMPTY BLADDER
Figure 3. Micturition reflex on an empty bladder.
There is about 10-20 mL of residual urine after
urination
Stretch receptors
o Located in the detrusor muscle
o Respond to a stretch of the bladder
(1) Nervous Involvement in the Micturition Reflex
Sacral region (S2-S4) of the spinal cord
Thoracolumbar (T11-L2) of the spinal cord
Pons
Pontine storage center AfraTafreeh.com
o Pontine micturition center
Cerebral cortex
(2) Pathways of Micturition Reflex on an Empty Bladder
(i) Hypogastric Nerve Pathway
(ii) Pathway of the Higher Brain Centers
Very little urine in the bladder AfraTafreeh.com
Ascending fibers from the sympathetic ganglion can
= minimal stretching detected by the stretch receptors
ascend to the higher brain centers.
= minimal activation of sensory afferent neurons
(Thoracolumbar region, pons, and ultimately the cerebral cortex)
→ ↓action potentials toward the sacral region of the spinal cord
o These tell the brain that the bladder is empty
The cerebral cortex activates the pontine storage center
Stimulate fibers that ascend to the thoracolumbar region (PSC) and inhibits the pontine micturition center (PMC)
Fibers come out and synapse on the preganglionic motor
neurons within the lateral gray horn of the spinal cord Pontine storage center sends descending fibers that:
o Stimulates preganglionic motor neurons
(sympathetic)
Inferior mesenteric ganglion project nerve fibers to the
detrusor muscle and the internal urethral sphincter
(hypogastric nerve)
o Inhibit the preganglionic motor neurons that are part
The hypogastric nerve releases norepinephrine to the
of the parasympathetic nerves in S2-S4
detrusor muscle and internal urethral sphincter.
Actions of norepinephrine:
o Norepinephrine binds to the β3 adrenergic receptors
on the detrusor muscle
Normally, when preganglionic motor neurons are
stimulated, they release acetylcholine (ACh) to the
detrusor muscle
o Norepinephrine binds to the α1 adrenergic receptor
o Cell bodies of the anterior gray horn
Part of the somatic nervous system
Releases ACh that binds to the nicotinic type 1
receptor on the external urethral sphincter
→ muscle contraction
• Voluntary control of the external urethral sphincter
2 of 6 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. MICTURITION REFLEX
Last edited: 6/23/2023
MICTURITION REFLEX
Renal | Micturition Reflex Medical Editor: Gerard Jude Loyola
OUTLINE
I) ANATOMY OF THE URINARY III) COMPOSITION OF URINE
BLADDER IV) SUPPLEMENTARY IMAGE
II) MICTURITION REFLEX V) REVIEW QUESTIONS
(A) DURING AN EMPTY BLADDER VI) REFERENCES
(B) DURING A FULL BLADDER
I) ANATOMY OF THE URINARY BLADDER
Detrusor muscle
o A thick muscular layer makes up the walls of the
bladder
Internal urethral sphincter
o Muscles surrounding the bladder neck
o Contracts during ejaculation to prevent retrograde
ejaculation of semen into the bladder [Moore, 2018]
o For females
External urethral sphincter
o Component of the urogenital diaphragm
o The striated muscle is located distally and inferiorly to
the bladder neck [Sam, Jiang & LaGrange, 2020]
Figure 1. Coronal section of the urinary bladder [Moore, 2018].
II) MICTURITION REFLEX
AfraTafreeh.com
Figure 2. Micturition reflex.
MICTURITION REFLEX RENAL PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 6
, (A) DURING AN EMPTY BLADDER
Figure 3. Micturition reflex on an empty bladder.
There is about 10-20 mL of residual urine after
urination
Stretch receptors
o Located in the detrusor muscle
o Respond to a stretch of the bladder
(1) Nervous Involvement in the Micturition Reflex
Sacral region (S2-S4) of the spinal cord
Thoracolumbar (T11-L2) of the spinal cord
Pons
Pontine storage center AfraTafreeh.com
o Pontine micturition center
Cerebral cortex
(2) Pathways of Micturition Reflex on an Empty Bladder
(i) Hypogastric Nerve Pathway
(ii) Pathway of the Higher Brain Centers
Very little urine in the bladder AfraTafreeh.com
Ascending fibers from the sympathetic ganglion can
= minimal stretching detected by the stretch receptors
ascend to the higher brain centers.
= minimal activation of sensory afferent neurons
(Thoracolumbar region, pons, and ultimately the cerebral cortex)
→ ↓action potentials toward the sacral region of the spinal cord
o These tell the brain that the bladder is empty
The cerebral cortex activates the pontine storage center
Stimulate fibers that ascend to the thoracolumbar region (PSC) and inhibits the pontine micturition center (PMC)
Fibers come out and synapse on the preganglionic motor
neurons within the lateral gray horn of the spinal cord Pontine storage center sends descending fibers that:
o Stimulates preganglionic motor neurons
(sympathetic)
Inferior mesenteric ganglion project nerve fibers to the
detrusor muscle and the internal urethral sphincter
(hypogastric nerve)
o Inhibit the preganglionic motor neurons that are part
The hypogastric nerve releases norepinephrine to the
of the parasympathetic nerves in S2-S4
detrusor muscle and internal urethral sphincter.
Actions of norepinephrine:
o Norepinephrine binds to the β3 adrenergic receptors
on the detrusor muscle
Normally, when preganglionic motor neurons are
stimulated, they release acetylcholine (ACh) to the
detrusor muscle
o Norepinephrine binds to the α1 adrenergic receptor
o Cell bodies of the anterior gray horn
Part of the somatic nervous system
Releases ACh that binds to the nicotinic type 1
receptor on the external urethral sphincter
→ muscle contraction
• Voluntary control of the external urethral sphincter
2 of 6 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. MICTURITION REFLEX