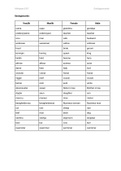
History of the debate: Precocial vs Atricial species:
Innatism; the theory that Precocial; species in which their young are relatively
behaviours are caused primarily by mature and mobile from the moment of birth/hatching.
biological causes (e.g. genes, DNA). Atricial; in which the young are incapable of moving
Environmentalism; the theory that around on their own soon after birth/hatching.
behaviours are caused by causes
from the environment (e.g. family,
friends, location). Concept of individual
differences:
The variation in human
traits.
Genetic determinism;
Nativism vs Empiricism:
people become who they
Biological traits are
are due to their genetic
inherited;
code.
- Colour of eyes
Environmentalism; we are
- Height and weight
who we are as a result of
- Facial characteristics
everyday experiences.
- Neurodegenerative
Genotype; collection of
disorders
genes, indicates which
- Neurodevelopment
genes are present.
- Down’s syndrome
- ASD
Nature and Phenotype; the apparent,
observable, measurable
- Attention. memory, nurture characteristics of the
language, maths,
individual (such as
reasoning, speed of
behaviour, height or
processing.
intelligence). It is the
product of the genetics as
Phenotypic plasticity;
well as the environment.
The degree to which the
phenotype is influenced by the Heritability:
environment. The degree of variation in
Low plasticity; genotype a phenotypic trait in a
exerts a strong influence so is population that is due to
independent of environmental genetic variation between
factors. individuals in that
High plasticity; genotype has population.
less influence.
Shared and non-shared environmental IQ:
effects: IQ has a normal distribution, with the average score
Shared environmental effects; aspects of being 100.
the environment that make children of MZ twins have a correlation for IQ of .87
the same family more similar. DZ twins have a .56 correlation.
Non-shared environmental effects; IQ has risen over time, roughly 3 points per decade
aspects of the environment that make (20 points since 1950).
them different. This could be due to reduction in family size,
nutrition, education, technology - slowing in
developing countries and rising in developing ones.
Innatism; the theory that Precocial; species in which their young are relatively
behaviours are caused primarily by mature and mobile from the moment of birth/hatching.
biological causes (e.g. genes, DNA). Atricial; in which the young are incapable of moving
Environmentalism; the theory that around on their own soon after birth/hatching.
behaviours are caused by causes
from the environment (e.g. family,
friends, location). Concept of individual
differences:
The variation in human
traits.
Genetic determinism;
Nativism vs Empiricism:
people become who they
Biological traits are
are due to their genetic
inherited;
code.
- Colour of eyes
Environmentalism; we are
- Height and weight
who we are as a result of
- Facial characteristics
everyday experiences.
- Neurodegenerative
Genotype; collection of
disorders
genes, indicates which
- Neurodevelopment
genes are present.
- Down’s syndrome
- ASD
Nature and Phenotype; the apparent,
observable, measurable
- Attention. memory, nurture characteristics of the
language, maths,
individual (such as
reasoning, speed of
behaviour, height or
processing.
intelligence). It is the
product of the genetics as
Phenotypic plasticity;
well as the environment.
The degree to which the
phenotype is influenced by the Heritability:
environment. The degree of variation in
Low plasticity; genotype a phenotypic trait in a
exerts a strong influence so is population that is due to
independent of environmental genetic variation between
factors. individuals in that
High plasticity; genotype has population.
less influence.
Shared and non-shared environmental IQ:
effects: IQ has a normal distribution, with the average score
Shared environmental effects; aspects of being 100.
the environment that make children of MZ twins have a correlation for IQ of .87
the same family more similar. DZ twins have a .56 correlation.
Non-shared environmental effects; IQ has risen over time, roughly 3 points per decade
aspects of the environment that make (20 points since 1950).
them different. This could be due to reduction in family size,
nutrition, education, technology - slowing in
developing countries and rising in developing ones.