KIDNEY DISEASE
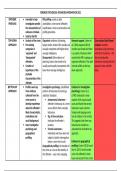
TYPES OF KIDNEY DISEASE
• Acute kidney Injury (AKI)
◦ Temporary kidney damage
◦ causes
▪ Myocardial infarction
▪ • Cardiac arrest (impaired kidney oxygenation)
• kidney is a metabolically demanding organ
▪ • Rhabdomyolysis
▪ • Decreased perfusion of the kidneys (e.g. blood loss or shock)
▪ • Obstruction along the urinary tract
▪ • Haemolytic uremic syndrome (E. coli infection)
▪ • Toxins • Glomerulonephritis
• Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
◦ permanent kidney damage
◦ causes
▪ Diabetic nephropathy
• linked with hypertension
▪ • Hypertension
▪ • Lupus (autoimmune disease)
▪ • Prolonged urinary tract obstruction
▪ • Alport syndrome (genetic)
▪ • Nephrotic syndrome
▪ • Polycystic kidney disease (genetic)
▪ • Cystinosis (genetic)
▪ • Interstitial nephritis or pyelonephritis
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD)
• CKD: Abnormal kidney structure or function, present for more than 3 months, with
a gradual loss of kidney function over months and years
,GLOBAL BURDEN OF CKD
• About 10% of the world population suffers from CKD
• •An estimated 5–10 million people die annually from kidney disease
• •Developed countries typically spend >2–3% of their annual healthcare budget for
dialysis and renal transplantation on <0.03% of the total population
CKD IN ENGLAND
• •More than 1.8 million people have been diagnosed with CKD
• • Estimated 1 million people with undiagnosed CKD
• •Annually 40,000 – 45,000 premature deaths due to CKD
• • £1.45 billion spent on CKD in 2010-11 (£1 for every £77 spent by the NHS)
SYMPTOMS OF CKD
, • 1-3 asymptomatic - mostly
◦ results in high population of undiagnosed CKD
• 4-5
◦ weight loss
◦ fatugue
◦ blood in urine
◦ insomnia
◦ muscle cramps
◦ nausea
◦ shortness of breath
DIAGNOSIS OF CKD
• • Blood tests for levels of creatinine and/or cystatin C → calculation of the
estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)
• eGFR using CKD-EPI: GFR = 141 * min(Scr/κ,1)α * max(Scr/κ, 1)-1.209 * 0.993Age *
1.018 [if female] * 1.159 [if black]
• •Urine tests → amount of albumin filtered in the urine
TYPES OF KIDNEY DISEASE
• Acute kidney Injury (AKI)
◦ Temporary kidney damage
◦ causes
▪ Myocardial infarction
▪ • Cardiac arrest (impaired kidney oxygenation)
• kidney is a metabolically demanding organ
▪ • Rhabdomyolysis
▪ • Decreased perfusion of the kidneys (e.g. blood loss or shock)
▪ • Obstruction along the urinary tract
▪ • Haemolytic uremic syndrome (E. coli infection)
▪ • Toxins • Glomerulonephritis
• Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
◦ permanent kidney damage
◦ causes
▪ Diabetic nephropathy
• linked with hypertension
▪ • Hypertension
▪ • Lupus (autoimmune disease)
▪ • Prolonged urinary tract obstruction
▪ • Alport syndrome (genetic)
▪ • Nephrotic syndrome
▪ • Polycystic kidney disease (genetic)
▪ • Cystinosis (genetic)
▪ • Interstitial nephritis or pyelonephritis
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD)
• CKD: Abnormal kidney structure or function, present for more than 3 months, with
a gradual loss of kidney function over months and years
,GLOBAL BURDEN OF CKD
• About 10% of the world population suffers from CKD
• •An estimated 5–10 million people die annually from kidney disease
• •Developed countries typically spend >2–3% of their annual healthcare budget for
dialysis and renal transplantation on <0.03% of the total population
CKD IN ENGLAND
• •More than 1.8 million people have been diagnosed with CKD
• • Estimated 1 million people with undiagnosed CKD
• •Annually 40,000 – 45,000 premature deaths due to CKD
• • £1.45 billion spent on CKD in 2010-11 (£1 for every £77 spent by the NHS)
SYMPTOMS OF CKD
, • 1-3 asymptomatic - mostly
◦ results in high population of undiagnosed CKD
• 4-5
◦ weight loss
◦ fatugue
◦ blood in urine
◦ insomnia
◦ muscle cramps
◦ nausea
◦ shortness of breath
DIAGNOSIS OF CKD
• • Blood tests for levels of creatinine and/or cystatin C → calculation of the
estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)
• eGFR using CKD-EPI: GFR = 141 * min(Scr/κ,1)α * max(Scr/κ, 1)-1.209 * 0.993Age *
1.018 [if female] * 1.159 [if black]
• •Urine tests → amount of albumin filtered in the urine