Organisation of the central nervous system
11 August 2020 10:14
What is the Central Nervous System?
• The human central nervous system contains the brain and spinal cord.
• The peripheral nervous system consists of: sensory neurons, clusters of neurons called ganglia and nerves connecting them to each other and to the CNS.
Central Nervous System:
3 Parts of the Brain:
1) Cerebrum (top part)
2) Cerebral Hemispheres (Left and Right)
3) Brainstem (connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord)
The Brainstem composed of 3 subparts: (Midbrain, Pons, Medulla oblongata)
Cerebellum located on the front, near the brainstem.
The names of the brain structures are developed from the names of the embryo from which they originate. For example:
○ Forebrain (consists of 3 major parts: cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, limbic system and olfactory bulb) (Prosencephalon)
○ Midbrain (consists of various cranial nerve nuclei, tectum etc.)(Mesencephalon)
○ Hindbrain (consists of brainstem made of medulla, pons, cerebellum, cranial nerves) (Rhombencephalon)
○ Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System:
The peripheral nervous system refers to parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord. It includes:
○ 12 cranial nerves (primarily comes out of the brain/skull)
○ 31 spinal nerves and their roots and branches (comes from the spine and pass through the CNS and PNS)
○ 43 pairs of peripheral nerves (motor and sensory)
○ Neuromuscular junctions
The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body.
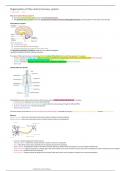
Neurons:
Afferent neurons- Axons carry information to the Central Nervous System from the peripheral.
Efferent neurons- Axons carry information from the Central nervous System to the peripheral.
○ Dendrites- Receives signals from other neurons
○ Cell body/ Soma - contains the nucleus and other structures common to living cells.
○ Axon - fibre which carries action potentials/ nerve impulses away from the cell body.
○ Myelin sheath - insulating layer made up of protein and fatty substances. Allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently.
○ Node of Ranvier (saltatory conduction) - periodic gap in the myelin sheath on the axon of certain neurons that serves to facilitate the rapid conduction of nerve impulses
○ Schwann cell - myelinate the axons of the PNS.
○ Axon terminal - Conducts electrical signals to nerve synapse which then moves across synapse to another axon via neurotransmitters.
Central Nervous System Page 1
11 August 2020 10:14
What is the Central Nervous System?
• The human central nervous system contains the brain and spinal cord.
• The peripheral nervous system consists of: sensory neurons, clusters of neurons called ganglia and nerves connecting them to each other and to the CNS.
Central Nervous System:
3 Parts of the Brain:
1) Cerebrum (top part)
2) Cerebral Hemispheres (Left and Right)
3) Brainstem (connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord)
The Brainstem composed of 3 subparts: (Midbrain, Pons, Medulla oblongata)
Cerebellum located on the front, near the brainstem.
The names of the brain structures are developed from the names of the embryo from which they originate. For example:
○ Forebrain (consists of 3 major parts: cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, limbic system and olfactory bulb) (Prosencephalon)
○ Midbrain (consists of various cranial nerve nuclei, tectum etc.)(Mesencephalon)
○ Hindbrain (consists of brainstem made of medulla, pons, cerebellum, cranial nerves) (Rhombencephalon)
○ Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System:
The peripheral nervous system refers to parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord. It includes:
○ 12 cranial nerves (primarily comes out of the brain/skull)
○ 31 spinal nerves and their roots and branches (comes from the spine and pass through the CNS and PNS)
○ 43 pairs of peripheral nerves (motor and sensory)
○ Neuromuscular junctions
The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body.
Neurons:
Afferent neurons- Axons carry information to the Central Nervous System from the peripheral.
Efferent neurons- Axons carry information from the Central nervous System to the peripheral.
○ Dendrites- Receives signals from other neurons
○ Cell body/ Soma - contains the nucleus and other structures common to living cells.
○ Axon - fibre which carries action potentials/ nerve impulses away from the cell body.
○ Myelin sheath - insulating layer made up of protein and fatty substances. Allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently.
○ Node of Ranvier (saltatory conduction) - periodic gap in the myelin sheath on the axon of certain neurons that serves to facilitate the rapid conduction of nerve impulses
○ Schwann cell - myelinate the axons of the PNS.
○ Axon terminal - Conducts electrical signals to nerve synapse which then moves across synapse to another axon via neurotransmitters.
Central Nervous System Page 1