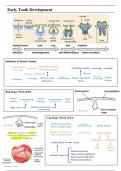
Transpiration And Water Uptake
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the leaves and stem of the
plant. That is a consequence of gaseous exchange as the stomata is open
this process can occur.
● Water also evaporates at the open stomata
● As the water molecules are attached to each other, when some
molecules leave the plant the rest of the molecules are pulled
through the xylem
● This results in more after being taken up by the soil resulting in a
continuous transpiration stream that travels through the plant
Translocation
Translocation the the movement of the food substances made up in the
leaves up or down the phloem for immediate use or even storage
● The phloem is found in the stems and the leaves
● There are elongated cells with holes in the cell wall
Structure of a xylem
The xylem vessels are made from dead xylem cells. These cells are made
up, and adapted to a specific function. They lose the end walls so the
xylem forms a continuous hollow tube
Structure of a phloem
Phloem vessels are made of living cells. The cell wall does not completely
break down. Instead sieve plates are formed - small holes in the end wall
which allows the dissolved sugars to pass through. The connection of
phloem cells effectively form a tube which enables dissolved sugars to be
transported.
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the leaves and stem of the
plant. That is a consequence of gaseous exchange as the stomata is open
this process can occur.
● Water also evaporates at the open stomata
● As the water molecules are attached to each other, when some
molecules leave the plant the rest of the molecules are pulled
through the xylem
● This results in more after being taken up by the soil resulting in a
continuous transpiration stream that travels through the plant
Translocation
Translocation the the movement of the food substances made up in the
leaves up or down the phloem for immediate use or even storage
● The phloem is found in the stems and the leaves
● There are elongated cells with holes in the cell wall
Structure of a xylem
The xylem vessels are made from dead xylem cells. These cells are made
up, and adapted to a specific function. They lose the end walls so the
xylem forms a continuous hollow tube
Structure of a phloem
Phloem vessels are made of living cells. The cell wall does not completely
break down. Instead sieve plates are formed - small holes in the end wall
which allows the dissolved sugars to pass through. The connection of
phloem cells effectively form a tube which enables dissolved sugars to be
transported.