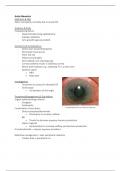
Definition & DDx
Optic neuropathy normally due to raised IOP
Anatomy & Risks
Predisposing factors
- Hypermetropia (long-sightedness)
- Pupillary dilatation
- Lens growth (age associated)
Symptoms & Complications
- Severe pain (ocular/headache)
- Decreased visual acuity
- Hard, red eye
- Haloes around lights
- Semi-dilated, non-reacting pupil
- Corneal oedema results in dull/hazy cornea
- Worse with mydriasis e.g., watching TV in a dark room
- Systemic upset
o N&V
o Abdo pain
Investigations
- Tonometry to assess for elevated IOP
- Gonioscopy
o Visualisation of the angle
Treatment/Management & Side effects
Urgent ophthalmology referral
- Analgesia
- Antiemetics
Combination of eye drops:
- Direct parasympathomimetic
o Pilocarpine to increase outflow
- BB
o Timolol to decrease aqueous humour production
- Alpha-2 agonist
o Apraclonidine to increase outflow and decrease production
IV acetazolamide – reduces aqueous secretions
Definitive management = laser peripheral iridotomy
- Creates hole in peripheral iris
,Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma
Definition & DDx
Optic neuropathy characterised by optic nerve fibre degradation
- With or without raised IOP
Anatomy & Risks
- Raised IOP
- HTN
- DM
- Steroids
- Myopia
- Afro-Caribbean
- Increasing age
- Genetics
Symptoms & Complications
Often no visual sx – diagnosed via screening
- Loss of peripheral fields
o ‘Tunnel vision’
- Decreased visual acuity
- Central scotoma (advanced)
Investigations
Fundoscopy/slit lamp
- Pale optic disc (indicates optic nerve atrophy)
- Optic disc cupping and pallor
o Ratio >0.7
- Retinal vessel ‘bayonetting’
o Vessels appear to have a break as they enter the deep cup
o Then reappear at the base (cup notching)
Tonometry IOP measurement = gold standard
Treatment/Management & Side effects
1st line = surgical management
- 360º selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT)
nd
2 line = medical management
- Latanoprost (PG analogue)
o Can increase eyelash length
o Brown pigmentation of iris
- Timolol (BB)
- Dorzolamide (carbonic anhydrase inhibitor)
- Brimonidine/apraclonidine (sympathomimetic)
o Avoid in TCA/MAOI
o Can cause hyperaemia
- Pilocarpine (miotic)
o Can cause pupil constriction, headache and blurred vision
, Blepharitis
Definition & DDx
Chronic inflammation of eyelid margins
Anatomy & Risks
- Staph
- HSV
- VZV
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Rosacea
Symptoms & Complications
- Painful, gritty, itchy eyes Investigations
- Eyelids sticking together upon Clinical diagnosis
waking
- Dry eye symptoms Treatment/Management & Side effects
- Erythema of eyelid margins No cure – rarely sight threatening
- Crusting/scaling - Lid hygiene BD
- Visibly blocked Meibomian gland o Softening lid margin using
orifices hot compresses
- Usually bilateral symptoms o Cooled boiled water and
- May have 2º conjunctivitis baby shampoo on cotton
- Styes/chalazions more common wool buds
- Avoid contacts during flare ups
- Artificial tears for symptom relief if
dry eyes
Benign Eyelid Disorders
Definition & DDx
Entropion = in-turning of eyelids
Ectropion = out-turning of eyelids
Anatomy & Risks
Stye (hordeolum) = infection of eyelid glands
- External = usually staph infection
- Internal = Meibomian gland infection
o Can leave residual chalazion
Chalazion (Meibomian cyst) = firm, painless lump in eyelid
- Normally resolve spontaneously
Symptoms & Complications
Stye = painful, red, hot lump
Chalazion = initially painful, evolves into non-tender swelling that points inwards
Treatment/Management & Side effects
Stye = hot compresses and analgesia; only abx TOP if associated conjunctivitis