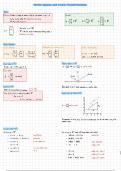
Vectors
Definition A vector is
simply an ordered n-tuple of real numbers VI , Va
, ...,
Un Examples :
2
V
, Va , ...,Un are called the components or entries of .
= = R
1
ERb
-
2 4
We has dimension a c E
say X n.
O
-
1
Vi
We write : E An
Va
V
R
=
-
is the set of all n-dimensional vectors called n
: ,
Un
dimensional real space .
Vector Operations
Vector Addition Multiplication by a scalar a ER Vector Substraction
V, qV,
a
WI Vi + wi
V2 Wa & V2
( w)
↓
Vatwa av V w =
V +
= =
t = -
+ w =
:
I
: :
in
:
Un Wn Vn + Wn XVn where -w is shorthand for 1-1) ef
Zero Vector in Ru Position Vectors in R2
A vector with n entries
equal to 0
. ↓ =
(Y) and w =
(w) as position vectors
Zero Vector
ya
O so(V , Val
8
8 =
In entries (W , Wa&
V
: q
W
8 -
E &
V X
Equality in Rh Every point (vi , va) is uniquely represented as a position vector.
Vectors are ordered tuples of numbers : (2) * (2)
Vector Let and w be victors in Rh General View of Vectors R2
Equality 1 in
Then1 =
w if
N *
y
V = Wi
, Va = Wa , ..., Un =
Wh V
-
4-
V =
Y as
free vector
3-
-vej -
2 -
------
*
i
1 - Vil =
M
= It's n
The components V, and
ve of 1 are viewed as displacements wrt .
the unit vectors i andj in the
coordinate system .
Laws for vectors in Rh
Let , V ,
we Rh L , X , we R" and a,B be any scalars (real numbers)
·
V + w =
W + V commutativity ·
x (V + w) = XV + xW distributivity
O
u + (k + w) = (u + 1) + w associativity ·
(x + B(v = xx + B
·
V + 0 =V & is the additive unit. ·
x(B1) =
(xB) mixed associativity
0 + k =
V · /k =
V multiply with 1
· + ( 1)
-
= 0 -
V is the additive inverse
(x) + V = Q Of Y · Ov =
0 multiply with scalar O
·
x0 =
0 multiply witha vector 3
·
(-Nk = (v) = x( x)
-
multiply with negatives