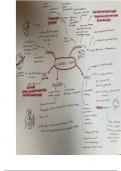
Normal reader: Dual-Route Cascaded (DRC) model:
- At least two different procedures – - Coltheart et al., (1993, 2001)
dual-route model - Lexical – representation and recognition
- Application of set of grapheme- o Orthographic input semantic
phoneme rules or by searching LTM for systems and phonological output
stored info. lexicon phoneme system
- Non-lexical – apply G-P conversion into
sound
Routes in reading: o Visual feature letter units G-
P rule system phoneme system
- Lexical – look up words in LTM to
(soundform) and access meaning
retrieve knowledge about meaning and
o Serial fashion – left-right
pronunciation
o Regularises irregular words =
o Direct retrieval of pronunciation
wrong pronunciation
o Can store regular, exception/
- Demands on route vary as a function of
irregular words
transparency of language
o Does NOT work for novel or
o Non-transparent = harder to read
non-words
as different strings have multiple
- Non-lexical – making use of rules
was to be read out loud.
relating segments of orthography and
More error rates
phonology
o G-P correspondence
o Approximation of novel words
o Does NOT work with irregular
words
Effects in the DRC and human readers:
1. Words read faster than non-words
2. High faster than low frequency
3. Regular words read faster and more
accurately than irregular words – no
conflict between lexical and non-lexical
route
4. Larger the orthographic neighbourhood
of non-words the faster it is read aloud
– if similar words in memory
5. Non-words that sound like words read
faster than those that don’t
6. More letters in a non-word the slower it
is to read aloud, not the case for words