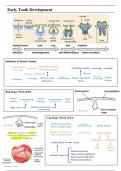
Initiation & Dental Lamina
Cranial Neural Dental Mesenchyme
Vestibular Lamina Vestibule
Crest Cells (Ectomesenchyme)
constant communication (buccal)
thickens (lingual) Dental
Primitive Oral Primary Epithelial
Ectoderm Lamina
Epithelium Band
Bud Stage (Week 8/10)
Dental Dental Tooth
Lamina swells Placodes proliferates Bud
BMPs, FGFs Epithelial-mesenchyme
communication
(Bud Stage)
Cap Stage (Week 11/12)
Dental mesenchyme condenses
(Cap Stage) Dental Papilla
below enamel organ
Slow differentiation in centre of Dental mesenchyme on
Dental Follicle
tooth bud & fast differentiation in sides of enamel organ
peripheries → cap shape
Fibroblasts Osteoblasts
Enamel Knot Cusps
PDL Alveolar
Stellate reticulum Bone
Enamel Organ Outer enamel epithelium
Inner enamel epithelium
Stratum intermedium
(Enamel Organ)
, Late Tooth Development
Enamel Organ Sonic Hedgehog (ssh)
• Stellate Reticulum: star-shaped cells with large intracellular spaces Expression
and many GAGs • Acts on transmembrane
• Outer Enamel Epithelium: many cuboidal cells in contact with protein PTCH1 to activate
dental follicle a signalling cascade
• Inner Enamel Epithelium: columnar cells • Expressed in epithelium
• Stratum Intermedium: flatted cells perpendicular to inner enamel of future incisors/molars
epithelium, between stellate reticulum and inner epithelium and tongue (for taste buds)
Bell Stage (Week 14/20) Dental Pulp Dental Papilla
remainder
Ameloblasts Enamel
Inner Enamel Odontoblasts
Epithelium Hertwig’s Epithelial
Cervical Loop proliferates
Root Sheath
Outer Enamel
Dental Follicle disintegrates Dentin
Epithelium
Epithelial Rests
Cementum of Malassez
Cementoblasts
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
• Required for bud → cap transition
• Activates cofactors to enhance
transcription of target genes
• BMP4 induces formation of
primary epithelial knot
Late Bell Stage
(Bell Stage) • Dental lamina breaks down and is disconnected from epithelium →
clusters of epithelial cells, which may persist into epithelial pearls
of Serres
• Stellate reticulum collapses at tip of cusp and outer enamel
epithelium brings blood vessels closer to ameloblasts for nutrients