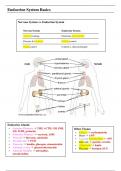
Nervous System vs. Endocrine System
Nervous System Endocrine System
Always working Functions intermittedly
Discrete & localised Diffuse control
Rapid control Control is often prolonged
Endocrine Glands
• Anterior Pituitary → TSH, ACTH, GH, FSH, Other Tissues
LH, ICSH, prolactin • Kidney → erythropoietin
• Posterior Pituitary → oxytocin, ADH • Heart → ANP
• Thyroid → thyroxin, calcitonin • Vascular Endothelium → vWF
• Parathyroid → PTH • Gut cells → gastrin, secretin
• Pancreas → insulin, glucagon, stomatostatin • Adipocytes → leptin
• Adrenal Cortex → glucocorticosteroids • Placenta → lactogen, hCG
• Adrenal Medulla → adrenaline,
noradrenaline
, Hormones
Peptide Hormones
• Polypeptides/glycoproteins
• The majority of hormones – includes all hormones of hypothalamus, pituitary,
parathyroids, pancreas & GI tract
• Synthesis: transcription + translation → preprohormone → cleave to prohormones
• Storage: in cells as granules in secretory vesicles (as prohormones)
• Transport: diffuse into leaky capillaries
• Half-life: short – polar / water-soluble → dissolve in plasma unbound
• Mechanism: bind to cell membrane receptors → secondary messenger activation
Steroid Hormones Eicosanoids
• Fat-soluble lipids derived from cholesterol • Local chemical messengers
• 3x 6-carbon rings & 1x 5-carbon ring • Exert a wide variety of effects in different
• Produced by adrenal glands, gonad & placenta organs & tissues
• Synthesis: in mitochondria & smooth ER • Autocrine or paracrine
• Storage: not stored – release depends on rate of • Derived from arachidonic acid (fatty acid)
synthesis
• Transport: diffuses across plasma membranes
• Half-life: long – circulates blood bound to Amine Hormones
proteins • Modified amino acids derived from
• Mechanism: binds to intracellular (nuclear) tyrosine
receptors → alters gene expression • Classified as thyroid or catecholamines
Thyroid Hormones Catecholamines
• Storage: in thyroid glands, bound to • Storage: intracellularly in secretory glands
thyroglobulin • Transport: water soluble – does not cross
• Transport: lipid-soluble – can cross plasma cell membrane
membranes • Half-life: short – circulates dissolved in
• Half-life: long – circulates blood bound to plasma unbound
proteins • Mechanism: binds to cell membrane
• Mechanism: binds to intracellular (nuclear) receptors → secondary messenger activation
receptors → alters gene expression
Hormone Storage Solubility Half-Life Receptor
Peptide Secretory vesicles Water-soluble Short Cell membrane
Released
Steroid Lipid-soluble Long Nuclear
immediately
Thyroid Thyroid gland Lipid-soluble Long Nuclear
Hormon
Amine
Catecholamine Secretory glands Water-soluble Short Cell membrane
, Pancreas
Islets of Langerhans
• Small, round clusters of cells embedded within exocrine
pancreas
• Cells smaller + more lightly stained than exocrine cells
• Main cell types:
o A → secrete glucagon (~20%)
o B → secrete insulin (~70%)
o D → secrete somatostatin (5-10%)
o F → secrete pancreatic polypeptide (1-2%) A Cells B Cells
(Glucagon) (Insulin)
Insulin Structure
• Peptide hormone
produced from
proinsulin
• A-chain with 21
amino acids
• B-chain with 30
amino acids
• Connected by 2
disulphide bonds
Glucagon Insulin
• Hyperglycaemic hormone, alongside • The only hypoglycaemic hormone (glucose →
adrenaline & cortisol (glycogen → glucose) glycogen)
• Secretion stimulated by low blood glucose, • Secretion stimulated by raised blood [glucose],
high blood [amino acid] & adrenaline raised blood [amino acid], secretin or glucagon
• Metabolic effects: • Metabolic effects:
o Mobilises fuel – maintains blood glucose o Promotes growth & food storage after
during fasting meal
o Activates glycogenolysis & o Stimulates glycogenesis (glycogen
gluconeogenesis in liver synthesis + storage)
o Activates uptake of amino acids by liver o Stimulates lipogenesis (fatty acid
for gluconeogenesis – transdeamination synthesis + storage from CHO) when
o Activates release of FA from adipose intake exceeds glycogen storing capacity
tissue and oxidation / ketone body o Stimulates amino acid uptake + protein
formation in liver synthesis