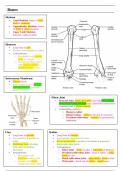
Bones
Skeleton
• Axial Skeleton: bones of head,
neck & vertebrae
• Appendicular Skeleton: bones
of limbs & pelvic skeleton
• Upper Limb Skeleton:
bumerus, radius & ulnar
Humerus
• Long bone in arm
• Extends from shoulder to elbow
• Articulations:
o Proximally with glenoid
fossa of scapula
o Distally (at elbow joint)
with head of radius &
trochlear notch of ulna
Interosseous Membrane
• Fibrous tissue
• Joints radius & ulna, actively
transferring force between
them
Elbow Joint
• Synovial Joint: freely moveable joint with ends of bone
covered by hyaline cartilage and a fluid-filled joint cavity
contained with a fibrous capsule
• Articulating surfaces:
o Humero-radial
o Humero-ulnar – hinge for flexion & extension
o Proximal radio-ulnar – rotation for pronation &
supination
Ulna Radius
• Long bone in forearm • Long bone in forearm
• Lies medially & parallel to • Lies laterally and parallel to ulna
radius • Pivots around ulna to produce movement at proximal /
• Stabilising bone, pivoting distal radio-ulnar joints
with radius to produce • Articulations:
movement o Elbow joint – head of radius + capitulum of humerus
• Articulations: o Proximal radio-ulnar joint – head of radius + radial
o Proximally with notch of ulna
humerus at elbow joint o Distal radio-ulnar joint – ulnar notch + head of ulna
o Distally with radius o Wrist joint – distal end of radius + carpal bones
(distal radio-ulnar joint)
Skeleton
• Axial Skeleton: bones of head,
neck & vertebrae
• Appendicular Skeleton: bones
of limbs & pelvic skeleton
• Upper Limb Skeleton:
bumerus, radius & ulnar
Humerus
• Long bone in arm
• Extends from shoulder to elbow
• Articulations:
o Proximally with glenoid
fossa of scapula
o Distally (at elbow joint)
with head of radius &
trochlear notch of ulna
Interosseous Membrane
• Fibrous tissue
• Joints radius & ulna, actively
transferring force between
them
Elbow Joint
• Synovial Joint: freely moveable joint with ends of bone
covered by hyaline cartilage and a fluid-filled joint cavity
contained with a fibrous capsule
• Articulating surfaces:
o Humero-radial
o Humero-ulnar – hinge for flexion & extension
o Proximal radio-ulnar – rotation for pronation &
supination
Ulna Radius
• Long bone in forearm • Long bone in forearm
• Lies medially & parallel to • Lies laterally and parallel to ulna
radius • Pivots around ulna to produce movement at proximal /
• Stabilising bone, pivoting distal radio-ulnar joints
with radius to produce • Articulations:
movement o Elbow joint – head of radius + capitulum of humerus
• Articulations: o Proximal radio-ulnar joint – head of radius + radial
o Proximally with notch of ulna
humerus at elbow joint o Distal radio-ulnar joint – ulnar notch + head of ulna
o Distally with radius o Wrist joint – distal end of radius + carpal bones
(distal radio-ulnar joint)