Thoracic Cavity
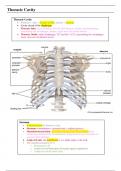
Thoracic Cavity
• Posterior + sides = 12 pairs of ribs; anterior = sternum
• Cavity closed off by diaphragm
• Thoracic Inlet: space bound by first rib, first thoracic vertebra and manubrium,
transmitting the oesophagus, trachea, vagus nerve & carotid arteries
• Thoracic Outlet: under diaphragm, T12 and ribs 11/12, transmitting the oesophagus,
aorta, vena cava & phrenic nerves
Sternum
• Anterior portion of thoracic cavity
• Sternum = manubrium + sternum body + xiphoid process
• Manubriosternal Joint: secondary cartilaginous-fibrocartilage joint,
connecting sternum body & manubrium, lying between synovial joints of
second costal cartilages
• Angle of Louis: the manubrium is at a slight angle to the body
• The manubriosternal level is:
o Horizontal to T4
o At the level of bifurcation of trachea (quiet respiration)
o At the level of the aortic arch
, Vertebral Column
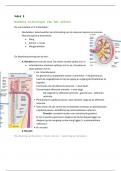
Vertebral Column
• 33 vertebrae connected by intervertebral discs, synovial joints, ligaments and muscles
Cervical Vertebra
• Consists of 7 distinct vertebrae, with 3 main characteristic features:
o Triangular vertebral foramen
o Bifid spinous process – where the spinous process splits into two distally
o Transverse foramina – gives passage to vertebral artery, vein and sympathetic nerves
Atlas (C1)
• No vertebral body & no spinous process
• Lateral masses, connected by an anterior and posterior arch
• Superior articular facet (articulates with occipital condyles) and inferior articular facet
(articulates with C2)
• Transverse ligament of the atlas secures a facet for articulation with the dens of the axis
• Groove on posterior arch for vertebral artery and C1 spinal nerve
Axis (C2)
• Odontoid Process (dens): extends superiorly from anterior portion and articulates with
anterior arch of atlas, creating the medial atlanto-axial joint
• Superior articular facets (articulates with inferior articular facets of C1)
Thoracic Cavity
• Posterior + sides = 12 pairs of ribs; anterior = sternum
• Cavity closed off by diaphragm
• Thoracic Inlet: space bound by first rib, first thoracic vertebra and manubrium,
transmitting the oesophagus, trachea, vagus nerve & carotid arteries
• Thoracic Outlet: under diaphragm, T12 and ribs 11/12, transmitting the oesophagus,
aorta, vena cava & phrenic nerves
Sternum
• Anterior portion of thoracic cavity
• Sternum = manubrium + sternum body + xiphoid process
• Manubriosternal Joint: secondary cartilaginous-fibrocartilage joint,
connecting sternum body & manubrium, lying between synovial joints of
second costal cartilages
• Angle of Louis: the manubrium is at a slight angle to the body
• The manubriosternal level is:
o Horizontal to T4
o At the level of bifurcation of trachea (quiet respiration)
o At the level of the aortic arch
, Vertebral Column
Vertebral Column
• 33 vertebrae connected by intervertebral discs, synovial joints, ligaments and muscles
Cervical Vertebra
• Consists of 7 distinct vertebrae, with 3 main characteristic features:
o Triangular vertebral foramen
o Bifid spinous process – where the spinous process splits into two distally
o Transverse foramina – gives passage to vertebral artery, vein and sympathetic nerves
Atlas (C1)
• No vertebral body & no spinous process
• Lateral masses, connected by an anterior and posterior arch
• Superior articular facet (articulates with occipital condyles) and inferior articular facet
(articulates with C2)
• Transverse ligament of the atlas secures a facet for articulation with the dens of the axis
• Groove on posterior arch for vertebral artery and C1 spinal nerve
Axis (C2)
• Odontoid Process (dens): extends superiorly from anterior portion and articulates with
anterior arch of atlas, creating the medial atlanto-axial joint
• Superior articular facets (articulates with inferior articular facets of C1)