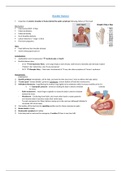
Impaction of anterior shoulder of foetus behind the pubic symphysis following delivery of the head
Risk Factors:
Macrosomia (EFW >4.5kg)
Maternal diabetes
Maternal obesity
Hx of shoulder dystocia
Labour dystocia (2nd stage >2-3hrs)
Post-term pregnancy
Signs
Head delivered but shoulder delayed
Turtle necking (goes back in)
Complications:
Asphyxiation (cord compression) Cerebral palsy or Death
Brachial plexus injury
- C5-C7 Erb-Duchenne Palsy - arm hangs limply at side of body, with forearm extended and internally rotated
(“Waiter’s tipp deformity)- only 1% are permanent
- C8-T1 Klumpke Palsy – Claw hand. Involvement of T1 may also show symptoms of Turner’s syndrome.
Management:
EMERGENCY
1) Identify problem immediately, call for help, and note the time (you have 5 mins to deliver the baby safely)
2) “Create space” (empty bladder, generous episiotomy, remove botom of bed) then manoeuvres:
3) McRoberts Manouvre - hyperflexing the motherss legs tightly to her abdomen which increases mobility at the SIJ.
o +/- Suprapubic pressure - aimed at rotating the baby’s anterior shoulder towards
its chest.
- Rubin manoeuvre – Insert fngers vaginally to rotate the baby’s anterior shoulder
towards its chest.
- Woodscrew – Continuing from Rubin, also insert other hand to rotate posterior
arm towards baby’s back thus rotate their entire body.
- Try each manoeuvre for 30secs before moving on to the next one (although McRobert’s
successful 90% of the time)
4) Get mother of the bed into the squatting position and try these manoeuvres again
5) Break clavicle of baby
6) Break pubic symphysis of mother
7) Push baby back in and send for emergency C-section (if there is any time lee)