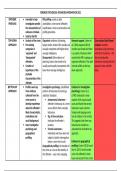
Linear Accelerators (LINACS) An AC Power supply is connected across
→ accelerates charged particles to each tube to ensure particles are always
very high speeds in straight lines. accelerated.
they use electric fields within - particles attract to midpoint of plate
metallic tubes which act as - A C supply will switch at middle
oppositely charged electrodes particles are repelled to exit and are
→ LINACS accelerate ions through attracted to next plate.
progressively long tubes connected - This process continues in a straight line
to an alternating power supply to to the end of accelerator.
ensure they are always accelerating
→ particles are kept in a linear path
by a series of magnets that force cyclotrons are made of:
drifting electrons to the centre of
a magnetic field. • two 'dees' (
Cyclotrons
→ uses magnetic fields and electric • a uniform magnetic field
fields to accelerate charged particles. • an AC power supply across
The magnetic fields keep the each dee which creates an
changed particles in a circular path electric field in the gap.
and electric field increases their speed.
magnetic field = keeps particles in magnetic field is perpendicular
circular path to the plane of dees
electric field = increases their speed
Process of accelerating an ion in a cyclotron: The alternating
- a source of charged particles is at centre potential difference
of cyclotron. is needed to accelerate
- particles fired into one dee particles across gap
- magnetic field makes particles follow a between opposite
circular path. electrodes
- P. d applied, accelerates particle to the next dee
due to electric field in the gap. The bigger the
- In next dee, particles continue to move in a cyclotron the
circular path within magnetic field. faster we can
- The particle then moves with an increasing make particles
radius depending on their velocity. travel.
- Eventually particles speed is large enough to
exit cyclotron in a straight ipath.
→ accelerates charged particles to each tube to ensure particles are always
very high speeds in straight lines. accelerated.
they use electric fields within - particles attract to midpoint of plate
metallic tubes which act as - A C supply will switch at middle
oppositely charged electrodes particles are repelled to exit and are
→ LINACS accelerate ions through attracted to next plate.
progressively long tubes connected - This process continues in a straight line
to an alternating power supply to to the end of accelerator.
ensure they are always accelerating
→ particles are kept in a linear path
by a series of magnets that force cyclotrons are made of:
drifting electrons to the centre of
a magnetic field. • two 'dees' (
Cyclotrons
→ uses magnetic fields and electric • a uniform magnetic field
fields to accelerate charged particles. • an AC power supply across
The magnetic fields keep the each dee which creates an
changed particles in a circular path electric field in the gap.
and electric field increases their speed.
magnetic field = keeps particles in magnetic field is perpendicular
circular path to the plane of dees
electric field = increases their speed
Process of accelerating an ion in a cyclotron: The alternating
- a source of charged particles is at centre potential difference
of cyclotron. is needed to accelerate
- particles fired into one dee particles across gap
- magnetic field makes particles follow a between opposite
circular path. electrodes
- P. d applied, accelerates particle to the next dee
due to electric field in the gap. The bigger the
- In next dee, particles continue to move in a cyclotron the
circular path within magnetic field. faster we can
- The particle then moves with an increasing make particles
radius depending on their velocity. travel.
- Eventually particles speed is large enough to
exit cyclotron in a straight ipath.