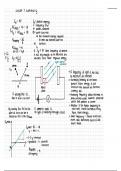
Lesson 1 summary
Ey - hf Eg = photon energy
f = frequency (Hz)
KE max = hf - 0 h= planks constant
GE2 = KEmaxt 0 1 = work function
↳ the minimum energy required
✓stopping = ¥ to emit one electron from the
hf surface.
451¥ Use If Ey < 0 then frequency of photon
[= F2 is not big enough so no electrons are
FEE Ey=h(£) emitted. can't have negative energy.
Light source
photon radiation
Eg
If frequency of light is too low,
KE Max no electrons are emitted.
oh • Increasing Intensity of the beam
e doesn't effect energy, it just
∅ metal increases the amount of electrons
plate coming off.
If voltage/Pid-0, • Increasing frequency allows electrons to
their is still a current A jump further across towards other side
which then produces a current-
• smaller 2 the higher frequency so
By turning the Pd to the If ammeter reads 0, electrons travel further as they
point of zero we see a no light is travelling through circuit. have more energy.
current as this is the KE max • lower frequency = slower electrons
move and therefore electric field
Ek Max stops them.
Ermast- hf - ∅
y = Moc + c
• (-) y-intercept
• gradient: h - planck's
f constant
Δ Ek Max
Δ frequency = h
Ey - hf Eg = photon energy
f = frequency (Hz)
KE max = hf - 0 h= planks constant
GE2 = KEmaxt 0 1 = work function
↳ the minimum energy required
✓stopping = ¥ to emit one electron from the
hf surface.
451¥ Use If Ey < 0 then frequency of photon
[= F2 is not big enough so no electrons are
FEE Ey=h(£) emitted. can't have negative energy.
Light source
photon radiation
Eg
If frequency of light is too low,
KE Max no electrons are emitted.
oh • Increasing Intensity of the beam
e doesn't effect energy, it just
∅ metal increases the amount of electrons
plate coming off.
If voltage/Pid-0, • Increasing frequency allows electrons to
their is still a current A jump further across towards other side
which then produces a current-
• smaller 2 the higher frequency so
By turning the Pd to the If ammeter reads 0, electrons travel further as they
point of zero we see a no light is travelling through circuit. have more energy.
current as this is the KE max • lower frequency = slower electrons
move and therefore electric field
Ek Max stops them.
Ermast- hf - ∅
y = Moc + c
• (-) y-intercept
• gradient: h - planck's
f constant
Δ Ek Max
Δ frequency = h