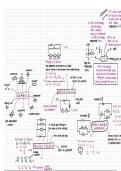
difference P-d is the trans
of electrical ener
to other forms pe
☆ Emf is the energy unit charge.
per unit charge measured in V
when chemical
energy is transferred
to electrical energy. EMF is the
measured in v. ideal pod is no
EMF internal resistance
VT V-IR
E-E E: EMF
r Q
Ri R2 R3
energy per un
v. = IR, v2- IR2 v3: IR}
E. M. F
↑
Resistors in series: they are
any component can be seen as a resistor inseparable Emf is the energy
ammeter SUM Of voltage in each resistor = total supply voltage = dots converted from some other
thermistor A
VT = V1 + V2 + V3 form to electrical potential
IRT = IR, + IR2 + IR3 ÷I current is the energy per coulomb charge
variable resistor ÷ ↳ current is constant all around so... same all around flowing through the source.
potentometer
switch RT = Re + R 2 + R3
series circuits
symbols ohmmeter
r e. g only one example ①
battery, cell VT LOOP
voltage distributed A parallel section
into components V1 V2 301
voltmeter VIV, + V2 401 * to + ¼
variable resistor
V Example ② 202 = ½ → 121
I0U
light dependable lov
add 121+401
resistor in each loop voltage is 301 401 series + paral et RT = 521
lor
the same as total voltage combination
201
10 V
more than one loop more current tra
Resistors in Parallel: towards the lower
1- add the resistors in the same line
-
I + = I, + -
T2 + I3 in parallel when it
-
It i. v = IT RT Parallel circuits current 30+40=701
701
RT = #+ to
IT = ¥ VIR splits at junctions
voltage: = ¼ 140 = 15.61
constant 201
=_
⇒¥ k.tk?+trs ÷v
= It = ½, + ½, + & answer
⇒ resistance = reciprocated
of electrical ener
to other forms pe
☆ Emf is the energy unit charge.
per unit charge measured in V
when chemical
energy is transferred
to electrical energy. EMF is the
measured in v. ideal pod is no
EMF internal resistance
VT V-IR
E-E E: EMF
r Q
Ri R2 R3
energy per un
v. = IR, v2- IR2 v3: IR}
E. M. F
↑
Resistors in series: they are
any component can be seen as a resistor inseparable Emf is the energy
ammeter SUM Of voltage in each resistor = total supply voltage = dots converted from some other
thermistor A
VT = V1 + V2 + V3 form to electrical potential
IRT = IR, + IR2 + IR3 ÷I current is the energy per coulomb charge
variable resistor ÷ ↳ current is constant all around so... same all around flowing through the source.
potentometer
switch RT = Re + R 2 + R3
series circuits
symbols ohmmeter
r e. g only one example ①
battery, cell VT LOOP
voltage distributed A parallel section
into components V1 V2 301
voltmeter VIV, + V2 401 * to + ¼
variable resistor
V Example ② 202 = ½ → 121
I0U
light dependable lov
add 121+401
resistor in each loop voltage is 301 401 series + paral et RT = 521
lor
the same as total voltage combination
201
10 V
more than one loop more current tra
Resistors in Parallel: towards the lower
1- add the resistors in the same line
-
I + = I, + -
T2 + I3 in parallel when it
-
It i. v = IT RT Parallel circuits current 30+40=701
701
RT = #+ to
IT = ¥ VIR splits at junctions
voltage: = ¼ 140 = 15.61
constant 201
=_
⇒¥ k.tk?+trs ÷v
= It = ½, + ½, + & answer
⇒ resistance = reciprocated