PHOTONS
particles of light (3×108)
Ey α frequency E=hf i:[initif 16.63×10-34)
Eg inversly proportional to 2 Eity
eV → J energy of photon units
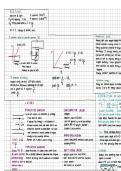
To estimate value of plancks constant (h): Photoelectric Effect:
shining light with enough energy onto
diode LED releases electrons causing current to
⟂
Energy of electrons depends on frequen
LED how intense. If energy intensity incr
A E- hf = he E-ev
ID ejection rate increases but KE Max
✓ 2
↓ ↓
same as well as original energy of
get = he V2: he
EYE:L a value which 0 current e Higher intensity = more photons
electron / 2
more electrons can absorb energy a
flows below it charge
depends on colour of LED released.
½ Energy transfer depends on freq
To improve accuracy: gradient:#= V2 Ionisation energy
repeat using various LED light colours
which emit different wavelengths of light gradxe - h energy an electron requires to escape
grad:#
plot a graph of V against ½ c leaving it as an ion- energy = positive
grad-⅓
REFRACTION OF WAV
↑! MV2 Misino, = Masino
LASERS :*:- R?-¥ air
0=
STIMULATED EMISSION SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS n, since - nzsin(90) sin (90
p ↳ occurs when an electron is already cheaper less optically dense → more
U in an excited state smaller, more efficient. light bends towards the norm
/ 2 If photon has energy = to difference in use less power so run on low voltage more optically dense → less o
MR MA electrons excited state and lower level it can used in DVD + CD players, barcode light bends away from normal
stimulate electron to drop down to lower scanners, laser printers
G
level releasing a second photon of equal TIR = TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECT
energy to the incoming photon. AMPILFYING MEDIUM occurs when angle of (i) is (>
E-hf C- 82 Photons are in phase , same energy. where stimulated emission takes place critical angle and when light is
E- he pumping process to a less optically dense me
2 POPULATION INVERSION
Ekmax-hf - 0 more electrons in upper than lower level SAFETY USING LASERS CLADDING
① -work function This is needed otherwise absorption has a higher • goggles with filter and lenses protects core preventing light to
minimum energy chance of taking place compared to stimulated • don't shine laser at reflective surfaces signal is accurate.
needed to eject an emission. • warn people allows TIR as it is a lower refra
electron from a • don't shine at a person
← cladd
surface. core
particles of light (3×108)
Ey α frequency E=hf i:[initif 16.63×10-34)
Eg inversly proportional to 2 Eity
eV → J energy of photon units
To estimate value of plancks constant (h): Photoelectric Effect:
shining light with enough energy onto
diode LED releases electrons causing current to
⟂
Energy of electrons depends on frequen
LED how intense. If energy intensity incr
A E- hf = he E-ev
ID ejection rate increases but KE Max
✓ 2
↓ ↓
same as well as original energy of
get = he V2: he
EYE:L a value which 0 current e Higher intensity = more photons
electron / 2
more electrons can absorb energy a
flows below it charge
depends on colour of LED released.
½ Energy transfer depends on freq
To improve accuracy: gradient:#= V2 Ionisation energy
repeat using various LED light colours
which emit different wavelengths of light gradxe - h energy an electron requires to escape
grad:#
plot a graph of V against ½ c leaving it as an ion- energy = positive
grad-⅓
REFRACTION OF WAV
↑! MV2 Misino, = Masino
LASERS :*:- R?-¥ air
0=
STIMULATED EMISSION SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS n, since - nzsin(90) sin (90
p ↳ occurs when an electron is already cheaper less optically dense → more
U in an excited state smaller, more efficient. light bends towards the norm
/ 2 If photon has energy = to difference in use less power so run on low voltage more optically dense → less o
MR MA electrons excited state and lower level it can used in DVD + CD players, barcode light bends away from normal
stimulate electron to drop down to lower scanners, laser printers
G
level releasing a second photon of equal TIR = TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECT
energy to the incoming photon. AMPILFYING MEDIUM occurs when angle of (i) is (>
E-hf C- 82 Photons are in phase , same energy. where stimulated emission takes place critical angle and when light is
E- he pumping process to a less optically dense me
2 POPULATION INVERSION
Ekmax-hf - 0 more electrons in upper than lower level SAFETY USING LASERS CLADDING
① -work function This is needed otherwise absorption has a higher • goggles with filter and lenses protects core preventing light to
minimum energy chance of taking place compared to stimulated • don't shine laser at reflective surfaces signal is accurate.
needed to eject an emission. • warn people allows TIR as it is a lower refra
electron from a • don't shine at a person
← cladd
surface. core