Cells and Immunity
Week 2
Phil Dash
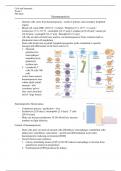
Haematopoiesis
- Immune cells come from haematopoiesis / reside in primary and secondary lymphoid
organs.
- Blood cell count; RBC [5x10^6 // 6-8µm] / Platelets [2.5 x 10^5 // 2-4 µm] /
Leukocytes [7.3 x 10^3] ~ neutrophil [12-15 µm]/ Lymphocyte [8-20 µm] / monocyte
[16-20 µm] / eosinophil [12-17 µm] / Basophil [12-15 µm]
- All cells are derived form bone marrow via haematopoiesis/ from common multi or
pluripotent stem cell population
- Stem cells divide into myeloid/ lymphoid progenitor [cells committed to specific
lineage] and differentiate in the bone marrow to
1. Myeloid;
granulocytes/
macrophages/
megakaryocyte
[platelets]/
erythrocytes
2. Lymphoid; T
cells/ B cells/ NK
cells
- Active bone marrow
haematopoiesis sites
within adults [skull/
sternum / ribs/
vertebrate/ pelvic/
iliac crest/ proximal
end of large bones]
Haematopoietic Homeostasis;
- Continuous process / production = loss
- Erythrocyte [120 days] / neutrophils [2-3 days] / T cells
[20-30 years]
- Body can increase production 10-20x blood loss increase
numbers to fight infection.
Control of haematopoiesis;
- Stem cells grow on mesh of stromal cells [fibroblasts/ macrophages/ endothelial cells/
adipocytes/ osteoblasts/ osteoclasts] = growth and differentiation as provides
haematopoietic inducing environment [HIM]
- Growth factors and cytokines;
1. Colony stimulating factors [CSF’s] M-CSF induces macrophage to develop from
granulocyte-monocyte progenitors.
2. Erythropoietin [EPO] produced by kidney.
Week 2
Phil Dash
Haematopoiesis
- Immune cells come from haematopoiesis / reside in primary and secondary lymphoid
organs.
- Blood cell count; RBC [5x10^6 // 6-8µm] / Platelets [2.5 x 10^5 // 2-4 µm] /
Leukocytes [7.3 x 10^3] ~ neutrophil [12-15 µm]/ Lymphocyte [8-20 µm] / monocyte
[16-20 µm] / eosinophil [12-17 µm] / Basophil [12-15 µm]
- All cells are derived form bone marrow via haematopoiesis/ from common multi or
pluripotent stem cell population
- Stem cells divide into myeloid/ lymphoid progenitor [cells committed to specific
lineage] and differentiate in the bone marrow to
1. Myeloid;
granulocytes/
macrophages/
megakaryocyte
[platelets]/
erythrocytes
2. Lymphoid; T
cells/ B cells/ NK
cells
- Active bone marrow
haematopoiesis sites
within adults [skull/
sternum / ribs/
vertebrate/ pelvic/
iliac crest/ proximal
end of large bones]
Haematopoietic Homeostasis;
- Continuous process / production = loss
- Erythrocyte [120 days] / neutrophils [2-3 days] / T cells
[20-30 years]
- Body can increase production 10-20x blood loss increase
numbers to fight infection.
Control of haematopoiesis;
- Stem cells grow on mesh of stromal cells [fibroblasts/ macrophages/ endothelial cells/
adipocytes/ osteoblasts/ osteoclasts] = growth and differentiation as provides
haematopoietic inducing environment [HIM]
- Growth factors and cytokines;
1. Colony stimulating factors [CSF’s] M-CSF induces macrophage to develop from
granulocyte-monocyte progenitors.
2. Erythropoietin [EPO] produced by kidney.