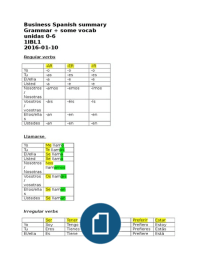
LO3.1 characterize and give examples for markets
Market:
Interactions between the buyer (deemandeers an dee seller (suppliers
Markets can be local, national, international
Price is deiscoverede in the interactions oo buyer ande seller
LO3.2 describe demand and explain how it can change
Demand:
Displayede in schedeule or a deemande curve
Shows the various amount oo a prodeuct that consumers are willing ande able to
purchase to goodes
o Amount consumers are willing ande able to purchase at a given price
o Willing ande able to buy because only willingness is not efective in the
market
Other things equal
Indeivideual deemande
Market deemande
Law of demand
= other things equal price oalls the quantity deemandeede rises ande as price
rises the quantity deemande oalls
Explanations
o Price acts as an obstacle to buyers
o Law oo deiminishing marginal utility
Big mac the seconde BM will yielde less satisoaction than the frst ect.
o Income efect ande substitution efect
Income effects occurs as a lower price increases the purchasing power oo money
income; this enables the consumer to buy more at a lower price (or
less at a higher price without having to redeuce consumption oo
other goodes.
Substitutions effect when a lower price gives an incentive to substitute the lower-pricede
goode oor the now relatively higher-pricede goodes.
The demand curve:
Illustrates the inverse relationship between price
ande quantity
Downwarde slope a lower quantity high price
Higher quantity lower price
o = both the law oo deemande
Market demand