INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY
Anatomical terminology
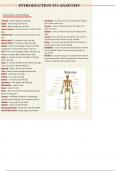
Transverse - splits the body in top and bottom Circumduction - the circular movement of a limb such that the distal
Sagittal - splits the body in left and right end of the limb creates an arc
Coronal - splits the body in front and back Pronation - occurs in the forearm only and is the twisting of the
Anterior / ventral - If a structure is closer to the front of the radius over the ulna
body Supination - occurs in the forearm only and is the realigning of the
Posterior/ dorsal - If a structure is closer to the back of the radius
body Inversion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement to
bring the plantar surface of the foot towards the midline
Inferior/ caudal - If a structure is closer to the feet
Eversion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement to
Superior/ cranial - If a structure is closer to the head
bring the plantar surface of the foot laterally
Proximal - This term is used largely in relation to the limbs,
Plantarflexion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement
and describes a structure which is closer to the trunk.
to bring the plantar surface of the foot posteriorly (going up on to
Distal - This term is used largely in relation to the limbs, and
your tip toes)
describes a structure which is further from the trunk
Dorsiflexion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement to
Medial - If a structure is closer to the midline of the body
bring the plantar surface of the foot anteriorly and to bring the dorsum
(such as the nose).
of the foot towards the anterior surface of the leg
Lateral - If a structure is further from the midline of the body
(such as the ears) it is described as lateral.
Superficial - Closer to the skin, and the surface.
Deep - Further from the skin, deeper inside the body
Bilateral - on both sides of the body
Unilateral - on one side of the body
Ipsilateral - on the same side of the body
Contralateral - on the opposite side of the body
Palmar surface - inside of a hand
Dorsum - outside of a hand
Flexion - refers to the movement which decreases the angle
between two body parts
Extension - the definition of extension is ‘increasing the
angle between two body parts’; it is the opposite of flexion.
Abduction - taking away from the midline
Adduction - bringing towards the midline
Internal/medial rotation - rotating a joint towards the midline
External/lateral rotation - rotating away from the midline
Anatomical terminology
Transverse - splits the body in top and bottom Circumduction - the circular movement of a limb such that the distal
Sagittal - splits the body in left and right end of the limb creates an arc
Coronal - splits the body in front and back Pronation - occurs in the forearm only and is the twisting of the
Anterior / ventral - If a structure is closer to the front of the radius over the ulna
body Supination - occurs in the forearm only and is the realigning of the
Posterior/ dorsal - If a structure is closer to the back of the radius
body Inversion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement to
bring the plantar surface of the foot towards the midline
Inferior/ caudal - If a structure is closer to the feet
Eversion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement to
Superior/ cranial - If a structure is closer to the head
bring the plantar surface of the foot laterally
Proximal - This term is used largely in relation to the limbs,
Plantarflexion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement
and describes a structure which is closer to the trunk.
to bring the plantar surface of the foot posteriorly (going up on to
Distal - This term is used largely in relation to the limbs, and
your tip toes)
describes a structure which is further from the trunk
Dorsiflexion - occurs at the ankle joint and describes the movement to
Medial - If a structure is closer to the midline of the body
bring the plantar surface of the foot anteriorly and to bring the dorsum
(such as the nose).
of the foot towards the anterior surface of the leg
Lateral - If a structure is further from the midline of the body
(such as the ears) it is described as lateral.
Superficial - Closer to the skin, and the surface.
Deep - Further from the skin, deeper inside the body
Bilateral - on both sides of the body
Unilateral - on one side of the body
Ipsilateral - on the same side of the body
Contralateral - on the opposite side of the body
Palmar surface - inside of a hand
Dorsum - outside of a hand
Flexion - refers to the movement which decreases the angle
between two body parts
Extension - the definition of extension is ‘increasing the
angle between two body parts’; it is the opposite of flexion.
Abduction - taking away from the midline
Adduction - bringing towards the midline
Internal/medial rotation - rotating a joint towards the midline
External/lateral rotation - rotating away from the midline