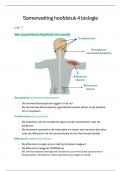
, Multiple-Choice Test Problems
Chapter 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts
Çengel/Boles - Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 8 th Edition
(Numerical values for solutions can be obtained by copying the EES solutions given and pasting them on
a blank EES screen, and pressing the Solve command. Similar problems and their solutions can be
obtained easily by modifying numerical values.)
Chap1-1 Pressure Difference in Water (Submarine)
Consider a submarine cruising 30 m below the free surface of seawater whose density is 1025 kg/m 3.
The increase in the pressure exerted on the submarine when it dives to a depth of 110 m below the free
surface is
(a) 480 kPa (b) 804 kPa (c) 1400 kPa (d) 144 kPa (e) 1100 kPa
Answer (b) 804 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=1025 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
z1=30 "m"
z2=110 "m"
DELTAP=rho*g*(z2-z1)/1000 "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=rho*g*(z2-z1) "not dividing by 1000"
W2=rho*g*(z1+z2)/1000 "adding depts instead of subtracting"
W3=rho*(z1+z2)/1000 "not using g"
W4=rho*g*(0+z2)/1000 "ignoring z1"
Chap1-2 Pressure Difference in Water (Lake)
Consider an 85-m deep lake. The pressure difference between the top and bottom of the lake is
(a) 834 kPa (b) 85 kPa (c) 417 kPa (d) 1220 kPa (e) 2430 kPa
Answer (a) 834 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=1000 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
z1=0 "m"
z2=85 "m"
DELTAP=rho*g*(z2-z1)/1000 "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=rho*(z1+z2)/1000 "not using g"
W2=rho*g*(z2-z1)/2000 "taking half of z"
,Chap1-3 Pressure Difference in Air (Mountain)
The atmospheric pressures at the top and the bottom of a mountain are read by a barometer to be 93.8
and 100.5 kPa. If the average density of air is 1.25 kg/m 3, the height of the mountain is
(a) 5360 m (b) 683 m (c) 547 m (d) 8200 m (e) 7650 m
Answer (c) 547 m
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=1.25 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s^2"
P1=93.8 "kPa"
P2=100.5 "kPa"
DELTAP=P2-P1 "kPa"
DELTAP=rho*g*h/1000 "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
DELTAP=rho*W1/1000 "not using g"
DELTAP=g*W2/1000 "not using rho"
P2=rho*g*W3/1000 "ignoring P1"
P1=rho*g*W4/1000 "ignoring P2"
Chap1-4 Oil Manometer (Duct)
The pressure drop in a duct is to be measured by a differential oil manometer. If the differential height
between the two fluid columns is 3.2 cm and the density of oil is 860 kg/m 3, the pressure drop in the duct
is
(a) 28 Pa (b) 135 Pa (c) 482 Pa (d) 270 Pa (e) 760 Pa
Answer (d) 270 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=860 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
h=0.032 "m"
DELTAP=rho*g*h "Pa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=rho*h "not using g"
W2=rho*g*h/2 "taking half of z"
Chap1-5 Gage-Absolute Pressure
A pressure gage connected to a tank reads 55 kPa at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 72.1
cmHg. The density of mercury is 13,600 kg/m 3. The absolute pressure in the tank is
(a) 41 kPa (b) 56 kPa (c) 82 kPa (d) 246 kPa (e) 151 kPa**
, Answer (e) 151 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=13600 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
h=0.721 "m"
Pgage=55 "kPa"
Patm=rho*g*h/1000 "kPa"
Pabs=Pgage+Patm "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=Patm-Pgage "taking the difference"
W2=Pgage+h "using h instead of Patm"
Chap1-6 Pressure rise due to Piston Weight
The pressure of a gas in a well-sealed vertical frictionless piston-cylinder device is to be increased by
adding a mass of 25 kg on the piston. If the diameter of the cylinder is 14 cm, the increase in the
pressure of the gas is
(a) 15.9 kPa (b) 0.25 kPa (c) 0.56 kPa (d) 1.8 kPa (e) 38.7 kPa
Answer (a) 15.9 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
m=25 "kg"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
W=m*g/1000 "kN"
D=0.14 "m"
A=pi*D^2/4 "m^2"
P=W/A "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=W "Ignoring piston area"
W2=W/D "using D instead of A"
W3=W/(pi*D) "using perimeter instead of area"
Chap1-7 Unit conversion (per C vs. F)
An orange loses 1.2 kJ of heat as it cools per C drop in its temperature. The amount of heat loss from
the orange per F drop in its temperature is
(a) 1.8 kJ (b) 1.0 kJ (c) 3.2 kJ (d) 2.1 kJ (e) 4.5 kJ
Answer (b) 1.0 kJ
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
Q_perC=1.8 "kJ"
Chapter 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts
Çengel/Boles - Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 8 th Edition
(Numerical values for solutions can be obtained by copying the EES solutions given and pasting them on
a blank EES screen, and pressing the Solve command. Similar problems and their solutions can be
obtained easily by modifying numerical values.)
Chap1-1 Pressure Difference in Water (Submarine)
Consider a submarine cruising 30 m below the free surface of seawater whose density is 1025 kg/m 3.
The increase in the pressure exerted on the submarine when it dives to a depth of 110 m below the free
surface is
(a) 480 kPa (b) 804 kPa (c) 1400 kPa (d) 144 kPa (e) 1100 kPa
Answer (b) 804 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=1025 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
z1=30 "m"
z2=110 "m"
DELTAP=rho*g*(z2-z1)/1000 "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=rho*g*(z2-z1) "not dividing by 1000"
W2=rho*g*(z1+z2)/1000 "adding depts instead of subtracting"
W3=rho*(z1+z2)/1000 "not using g"
W4=rho*g*(0+z2)/1000 "ignoring z1"
Chap1-2 Pressure Difference in Water (Lake)
Consider an 85-m deep lake. The pressure difference between the top and bottom of the lake is
(a) 834 kPa (b) 85 kPa (c) 417 kPa (d) 1220 kPa (e) 2430 kPa
Answer (a) 834 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=1000 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
z1=0 "m"
z2=85 "m"
DELTAP=rho*g*(z2-z1)/1000 "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=rho*(z1+z2)/1000 "not using g"
W2=rho*g*(z2-z1)/2000 "taking half of z"
,Chap1-3 Pressure Difference in Air (Mountain)
The atmospheric pressures at the top and the bottom of a mountain are read by a barometer to be 93.8
and 100.5 kPa. If the average density of air is 1.25 kg/m 3, the height of the mountain is
(a) 5360 m (b) 683 m (c) 547 m (d) 8200 m (e) 7650 m
Answer (c) 547 m
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=1.25 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s^2"
P1=93.8 "kPa"
P2=100.5 "kPa"
DELTAP=P2-P1 "kPa"
DELTAP=rho*g*h/1000 "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
DELTAP=rho*W1/1000 "not using g"
DELTAP=g*W2/1000 "not using rho"
P2=rho*g*W3/1000 "ignoring P1"
P1=rho*g*W4/1000 "ignoring P2"
Chap1-4 Oil Manometer (Duct)
The pressure drop in a duct is to be measured by a differential oil manometer. If the differential height
between the two fluid columns is 3.2 cm and the density of oil is 860 kg/m 3, the pressure drop in the duct
is
(a) 28 Pa (b) 135 Pa (c) 482 Pa (d) 270 Pa (e) 760 Pa
Answer (d) 270 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=860 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
h=0.032 "m"
DELTAP=rho*g*h "Pa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=rho*h "not using g"
W2=rho*g*h/2 "taking half of z"
Chap1-5 Gage-Absolute Pressure
A pressure gage connected to a tank reads 55 kPa at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 72.1
cmHg. The density of mercury is 13,600 kg/m 3. The absolute pressure in the tank is
(a) 41 kPa (b) 56 kPa (c) 82 kPa (d) 246 kPa (e) 151 kPa**
, Answer (e) 151 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
rho=13600 "kg/m^3"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
h=0.721 "m"
Pgage=55 "kPa"
Patm=rho*g*h/1000 "kPa"
Pabs=Pgage+Patm "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=Patm-Pgage "taking the difference"
W2=Pgage+h "using h instead of Patm"
Chap1-6 Pressure rise due to Piston Weight
The pressure of a gas in a well-sealed vertical frictionless piston-cylinder device is to be increased by
adding a mass of 25 kg on the piston. If the diameter of the cylinder is 14 cm, the increase in the
pressure of the gas is
(a) 15.9 kPa (b) 0.25 kPa (c) 0.56 kPa (d) 1.8 kPa (e) 38.7 kPa
Answer (a) 15.9 kPa
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
m=25 "kg"
g=9.81 "m/s2"
W=m*g/1000 "kN"
D=0.14 "m"
A=pi*D^2/4 "m^2"
P=W/A "kPa"
“Some Wrong Solutions with Common Mistakes:”
W1=W "Ignoring piston area"
W2=W/D "using D instead of A"
W3=W/(pi*D) "using perimeter instead of area"
Chap1-7 Unit conversion (per C vs. F)
An orange loses 1.2 kJ of heat as it cools per C drop in its temperature. The amount of heat loss from
the orange per F drop in its temperature is
(a) 1.8 kJ (b) 1.0 kJ (c) 3.2 kJ (d) 2.1 kJ (e) 4.5 kJ
Answer (b) 1.0 kJ
Solution Solved by EES Software. Solutions can be verified by copying-and-pasting the following lines
on a blank EES screen.
Q_perC=1.8 "kJ"