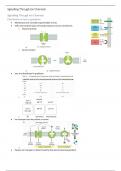
Signalling Through Ion Channels
Distribution of ions in gradients
• Membranes are normally impermeable to ions
• Cells have evolved ways of transporting ions across membranes
o Channel protein
▪
o Carrier protein
▪
• Ions are distributed in gradients
o
o
• Ion transport can be passive or active
o
• Passive ion transport is determined by the electrochemical gradient
,Signalling Through Ion Channels
o
• Summary
o Ions exist in gradients across both the PM and organelles
o Ion transport is effected by transporters and ion channels
o Transport can be passive or active
How ion gradients are generated ways
• Ion gradients are generated by active transport
o Active transport requires ATP
▪
• Ions are distributed in gradients
o Na / K gradient
▪
▪ Na/K pump generates Na and K gradients across the plasma membrane
•
o Pump embedded in membrane
o ATP → ADP + Pi
o 3Na ejected out of cell + 2K brought into cell = generating Na and K gradient
▪ Na – higher concentration outside
▪ K – higher concentration inside
• Na/K pump = P-type ATPase (phosphorylation)
, Signalling Through Ion Channels
o
o Pump phosphorylated in response to ATP hydrolysis
▪ Resting state
• Pump in particular confirmation – with binding site for 3Na
▪ ATP hydrolysed to ADP
• Phosphorylates pump
▪ Confirmational change = Na ions leave cell
▪ 2K ions bind to new confirmation
▪ Pump is dephosphorylated
• Phosphate unbinds
▪ K ions enter cell
o Ca gradient
▪
▪ Ca pumps generate Ca gradients across the plasma membrane
•
•
Plasma membrane Ca ATPase (PMCA) – P-type ATPase
o Phosphorylated = active – transports Ca out of cell
▪ Ca pumps generate Ca gradients across intracellular stores