Week 5 Computer Systems Lecture: Flowchart and Pseudocode 13.02.23
Video
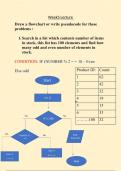
First part of flowchart is to input a number
Then a second number
Then the flowchart will ask a question
The flowchart will then branch the output
Make sure you know what shapes should be used in the flowchart
Pseudocode is an alternative way to represent the sequence in an algorithm
The instructions match up to the flow chart e.g. INPUT number 1
Flowcharts
Diagram that represents workflow or process
Can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step
approach to solving a task
X = Price, Y = Price 2
If the price of product 1 is bigger than the price of product 2, print X. Otherwise print Y, then
stop
If X and Y are the same price, you will get an error. You have to do another branch e.g. if X
=Y, you need to print X and Y are the same
You can also write if X=Y or if X>Y and this can go to one branch
The flowchart shows the steps as boxes of various kinds, they are ordered by connecting the
boxes with arrows
This diagrammatic representation illustrates a solution model to a given problem
Flowcharts are used in analysing, designing, documenting or managing a process or program
in various fields
Example of customer credit
Need to add Start and Finish
Buy product - Credit form Order form Credit check If the credit check is good
Review accounts receivable balance. If credit check is not good back to sales call
You can only have two arrows from every statement e.g. yes/no, true/false, 1/2
If you need more than two arrows, you need to add another statement
Flowchart (Loop statement While/do while)
Between the input and output there is a processing stage
While – you have a condition (true or false) e.g. while I = < 5 and you want to change. Check
the task, then check
Do while – I < 5, check the file, then do the task
For – you need 3 things: initial value, last value and increment or decrement value
Loop – the arrow loops back to the start. Do while – the loop stems from the condition,
While loop – the arrow stems from the task
Over 60 working example Python
And is the same as multiplying e.g. 0 and 1 is 1
If the condition is false you will not get anything in the output
0 or 1 is 1
Video
First part of flowchart is to input a number
Then a second number
Then the flowchart will ask a question
The flowchart will then branch the output
Make sure you know what shapes should be used in the flowchart
Pseudocode is an alternative way to represent the sequence in an algorithm
The instructions match up to the flow chart e.g. INPUT number 1
Flowcharts
Diagram that represents workflow or process
Can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step
approach to solving a task
X = Price, Y = Price 2
If the price of product 1 is bigger than the price of product 2, print X. Otherwise print Y, then
stop
If X and Y are the same price, you will get an error. You have to do another branch e.g. if X
=Y, you need to print X and Y are the same
You can also write if X=Y or if X>Y and this can go to one branch
The flowchart shows the steps as boxes of various kinds, they are ordered by connecting the
boxes with arrows
This diagrammatic representation illustrates a solution model to a given problem
Flowcharts are used in analysing, designing, documenting or managing a process or program
in various fields
Example of customer credit
Need to add Start and Finish
Buy product - Credit form Order form Credit check If the credit check is good
Review accounts receivable balance. If credit check is not good back to sales call
You can only have two arrows from every statement e.g. yes/no, true/false, 1/2
If you need more than two arrows, you need to add another statement
Flowchart (Loop statement While/do while)
Between the input and output there is a processing stage
While – you have a condition (true or false) e.g. while I = < 5 and you want to change. Check
the task, then check
Do while – I < 5, check the file, then do the task
For – you need 3 things: initial value, last value and increment or decrement value
Loop – the arrow loops back to the start. Do while – the loop stems from the condition,
While loop – the arrow stems from the task
Over 60 working example Python
And is the same as multiplying e.g. 0 and 1 is 1
If the condition is false you will not get anything in the output
0 or 1 is 1