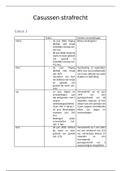
2.2
PRE TRIAL
- Pre-trial is the process of forming decisions through the Magistrates Court before
the trial is heard.
- The pre-trial decisions usually include reviewing if evidence is admissible.
- There are 3 types of offences: Indictable offences, Triable either way offences and
Summary offences.
- Indictable offences are serious crimes such as murder, GBH and robbery.
- These are tried in the Crown Court.
- ABH, Fraud and theft are classified as Triable either way offences, these are
perceived as the middle category of crime.
- Depending on the complexity and severity of the crime, it will be tried in the Crown
court, however in most cases the case will be heard in a Magistrates Court.
- Summary offences stay in the Magistrates court as they mainly deal with minor
offences.
- when dealing with minor offences, a document that contains the date they must
attend court is sent to the defendant.
- This is called being Summoned.
- However, a charge is done verbally by the police when they are arrested, they are
then given a charge sheet for serous crimes.
- All criminal cases are initially heard In a Magistrates Court where 95% of cases
usually stay there.
BAIL
- Bail is when the defendant is released until their hearing.
- This is granted under the Bail Act 1976. Bail is commonly granted unless, they have
broken bail before, they believe they are likely to reoffend, or they don’t think they
will show up to the hearing.
- Bail is granted by the police or the courts.
- There may be some rules such as having a curfew when released on bail.
- Sureties are people who guarantee the defendant will turn up on the given date,
however, if they don’t appear the sureties will keep the money given by the
defendant that the amount for bail was required.
PLEA BARGAINING
- Plea bargaining aims to decide how the defendant will plea and the most
appropriate measures in how the court should respond.
- Plea bargaining is when the prosecution and defence or judge before the trial agree
for the defendant to plead guilty.
- The defence usually bargains to reduce the charge or deduct specific charges.
- Court bargaining is when they negotiate how many charges someone will face.
- For example, they will plead guilty to manslaughter instead of murder or they will
plead guilty to 1 in return for others to be neglected.
- However, charge bargaining is when they receive a lesser sentence if they plead
guilty to the less serious charge.
- However, in some cases, sentence bargaining means if the offender just pleads
guilty, they will get a slightly more lenient charge than if they plead not guilty.
PRE TRIAL
- Pre-trial is the process of forming decisions through the Magistrates Court before
the trial is heard.
- The pre-trial decisions usually include reviewing if evidence is admissible.
- There are 3 types of offences: Indictable offences, Triable either way offences and
Summary offences.
- Indictable offences are serious crimes such as murder, GBH and robbery.
- These are tried in the Crown Court.
- ABH, Fraud and theft are classified as Triable either way offences, these are
perceived as the middle category of crime.
- Depending on the complexity and severity of the crime, it will be tried in the Crown
court, however in most cases the case will be heard in a Magistrates Court.
- Summary offences stay in the Magistrates court as they mainly deal with minor
offences.
- when dealing with minor offences, a document that contains the date they must
attend court is sent to the defendant.
- This is called being Summoned.
- However, a charge is done verbally by the police when they are arrested, they are
then given a charge sheet for serous crimes.
- All criminal cases are initially heard In a Magistrates Court where 95% of cases
usually stay there.
BAIL
- Bail is when the defendant is released until their hearing.
- This is granted under the Bail Act 1976. Bail is commonly granted unless, they have
broken bail before, they believe they are likely to reoffend, or they don’t think they
will show up to the hearing.
- Bail is granted by the police or the courts.
- There may be some rules such as having a curfew when released on bail.
- Sureties are people who guarantee the defendant will turn up on the given date,
however, if they don’t appear the sureties will keep the money given by the
defendant that the amount for bail was required.
PLEA BARGAINING
- Plea bargaining aims to decide how the defendant will plea and the most
appropriate measures in how the court should respond.
- Plea bargaining is when the prosecution and defence or judge before the trial agree
for the defendant to plead guilty.
- The defence usually bargains to reduce the charge or deduct specific charges.
- Court bargaining is when they negotiate how many charges someone will face.
- For example, they will plead guilty to manslaughter instead of murder or they will
plead guilty to 1 in return for others to be neglected.
- However, charge bargaining is when they receive a lesser sentence if they plead
guilty to the less serious charge.
- However, in some cases, sentence bargaining means if the offender just pleads
guilty, they will get a slightly more lenient charge than if they plead not guilty.