NASM – Flexibility test with correct answers
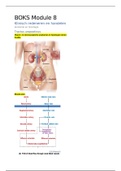
Flexibility The normal extensibility of soft tissues that allows for full range of motion of a joint. Extensibility Capability to be elongated or stretched. Range of motion The degree to which specific joints or body segments can move; often measured in degrees. Joint ROM is dictated by the type of joint (e.g., ball-and-socket versus hinge joint), and the extensibility of muscles and surrounding soft tissues Mobility Optimal flexibility and joint range of motion; ability to move freely. Relative flexibility The process in which the body seeks the path of least resistance during functional movements. Soft Tissue Tissue connecting, supporting, and surrounding bodily structures and organs. Myofascial The body's connective tissue that includes muscles and fascia. Postural distortion patterns Predictable patterns of muscle imbalances Muscle imbalance When muscles on each side of a joint have altered length-tension relationships. Alterations in the lengths of muscles surrounding a joint in which some are overactive (forcing compensation to occur) and others may be underactive (allowing for the compensation to occur Force-couple relationship The synergistic action of multiple muscles working together to produce movement around a joint. Osteokinematics Movement of a limb that is visible Arthrokinematics The description of joint surface movement; consists of three major types: roll, slide, and spin. Reciprocal inhibition When an agonist receives a signal to contract, its functional antagonist also receives an inhibitory signal allowing it to lengthen. Altered reciprocal inhibition Occurs when an overactive agonist muscle decreases the neural drive to its functional antagonist. Overactive When elevated neural drive causes a muscle to be held in a chronic state of contraction. Underactive When a muscle is experiencing neural inhibition and limited neuromuscular recruitment. Synergistic dominance The neuromuscular phenomenon that occurs when synergists take over function for a weak or inhibited prime mover (agonist). Altered length-tension relationship When a muscle's resting length is too short or too long, reducing the amount of force it can produce. Neuromuscular efficiency The ability of the nervous system to recruit the correct muscles to produce force, reduce force, and dynamically stabilize the body's structure in all three planes of motion. Muscle spindle Sensory receptors sensitive to change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change. central nervous system A division of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord.
Written for
- Institution
- Havard School
- Module
- NASM Stretching and Flexibility
Document information
- Uploaded on
- October 14, 2023
- Number of pages
- 3
- Written in
- 2023/2024
- Type
- Exam (elaborations)
- Contains
- Questions & answers
Subjects
-
nasm flexibility test