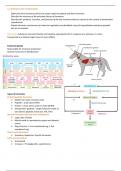
1.1 INTRODUCTION TO ENDOCRINE
Define the term hormone and list the major endocrine glands and their hormones
Describe the structure of the principal classes of hormones
Describe the synthesis, secretion, and function of the key hormones that are central to the control of mammalian
reproduction
Explain the basic mechanisms of endocrine regulation and feedback using the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal
axis as an example
Hormone = Substance secreted directly into blood by specialised cells in response to a stimulus, it is then
transported to a distant target tissue to exert effects
Endocrine glands
Responsible for hormone production
Secrete hormones to bloodstream
Types of hormones
Protein/peptide hormones
➢ Made from chain of amino acids
➢ Peptide = small chain (TRH)
➢ Protein = more amino acids in chain (GnRH)
➢ Glycoprotein peptide = Large moleucles made of
two distinct peptide chains (LH, FSH, TSH)
Steroid hormones (derived from cholesterol)
➢ Large class of lipids
➢ Mainly made in reproductive organs and adrenal
cortex
➢ Ring structure > 3 six membered ring, 1 five
membered ring
Amino acid derivatives
➢ Arenaline, dopamine, thyroid hormones
Fatty acid derivatives
➢ Eicosanoids
➢ 2 classes = Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes
Define the term hormone and list the major endocrine glands and their hormones
Describe the structure of the principal classes of hormones
Describe the synthesis, secretion, and function of the key hormones that are central to the control of mammalian
reproduction
Explain the basic mechanisms of endocrine regulation and feedback using the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal
axis as an example
Hormone = Substance secreted directly into blood by specialised cells in response to a stimulus, it is then
transported to a distant target tissue to exert effects
Endocrine glands
Responsible for hormone production
Secrete hormones to bloodstream
Types of hormones
Protein/peptide hormones
➢ Made from chain of amino acids
➢ Peptide = small chain (TRH)
➢ Protein = more amino acids in chain (GnRH)
➢ Glycoprotein peptide = Large moleucles made of
two distinct peptide chains (LH, FSH, TSH)
Steroid hormones (derived from cholesterol)
➢ Large class of lipids
➢ Mainly made in reproductive organs and adrenal
cortex
➢ Ring structure > 3 six membered ring, 1 five
membered ring
Amino acid derivatives
➢ Arenaline, dopamine, thyroid hormones
Fatty acid derivatives
➢ Eicosanoids
➢ 2 classes = Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes