Lecture 17 – neuro-imaging
Introduction;
- In 1990 Acceleration in research > ‘The decade of the brain’ & the acceleration of
neuroscience research
- The brain initiative - President Obama, April 2013
- Increase the public’s awareness of the need for brain research
- Specificity, mapping, differentiation of the sensory and cognitive systems of the
mature adult brain
- Before Brain imaging there was Post-mortem, Xray
- ‘Over the years, our understanding of the brain--how it works, what goes wrong
when it is injured or diseased--has increased dramatically. However, we still have
much more to learn. The need for continued study of the brain is compelling: millions
of Americans are affected each year by disorders of the brain ranging from
neurogenetic diseases to degenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's, as well as
stroke, schizophrenia, autism, and impairments of speech, language, and hearing’.
Bush, 1990
- This isn’t just basic science it has practical implications.
Techniques for assessing brain anatomy;
- CAT/MRI
Techniques for assessing physiological function;
- SPECT/PET/fMRI/EEG/ERP/MEG/NIRs
Techniques for modulating brain activity;
- TMS
CAT;
- Old technique assessing structural integrity but widely used
in hospitals
- Computerized axial tomography more often called CT today
- Dense tissue (e.g., bone) appears white
- Less dense (e.g., CSF) appears black
- A series of oblique slices of the brain (9-12)
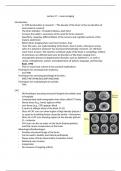
- Slices of CAT scan can show region of high density (picture 1
so, good at visualising lesion caused by stroke = Hematoma.
- Slices of a CAT scan showing regions of low density (picture
2) = Ischemia.
- CAT scan can also so water on the brain (hydrocephalus)
and that causes compression of the brain.
Advantages/disadvantages;
- Provides structural image of the brain
- Can be used in healthy and clinical participants
- Shows areas of brain abnormality (resolution 5mm)
- Relatively non-invasive
- Inexpensive
- No measure of ongoing activity
, MRI;
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Relies on magnetic fields to distort behaviour of protons
- Scanner is tuned to detect radio frequencies emitted from hydrogen atoms
- Different concentrations of hydrogen atoms in different tissue
- 3 different planes
- MRI and brain lesions
Necessary equipment;
- Big magnetic field = protons (hydrogen molecules) in body become aligned
to field.
- RF (radio frequency) coil = radio frequency pulse which knocks protons
over. As protons realign with field, they emit energy that coil receives (like
an antenna)
- Gradient coils = make it possible to encode spatial information.
- MRI produced really clear scans and so is more likely to find really small
lesions. It detects spatial resolutions of as small as 1mm.
Advantages;
- Non-invasive
- Clear structural images: Good spatial resolution (1-2mm)
- No known biological risk: Does not expose individual to X-rays
- Very good spatial resolution
Disadvantages;
- Claustrophobia
- Ferromagnetic materials / pacemakers!
- Good images hard to obtain near large cavities
- Tumours might be mistaken for cells with excess fluid
- Head placement / noisy
SPECT;
- Single photon emission computerised tomography
- Used to measure brain function
- Useful for damaged and intact brains
- Gamma emitting radioactive tracer
- SPECT measure brain’s uptake of radioactively labelled oxygen
- Sensitive to changes in blood flow
- Injection of radiopharmaceutical and scan after 30 mins
- Neural activity in related to increase in demand for blood so,
rather than a direct measurement it capitalises on the idea that
if an area is demanding more fuel then we can make the link that this area is been
more active.
Alzheimer’s Disease;
- 72 year old man with history of progressive short term memory loss
- Bilateral cortical perfusion defects involving the temporal and
parietal lobes
- Shows BLOOD FLOW DEFICITS.
Introduction;
- In 1990 Acceleration in research > ‘The decade of the brain’ & the acceleration of
neuroscience research
- The brain initiative - President Obama, April 2013
- Increase the public’s awareness of the need for brain research
- Specificity, mapping, differentiation of the sensory and cognitive systems of the
mature adult brain
- Before Brain imaging there was Post-mortem, Xray
- ‘Over the years, our understanding of the brain--how it works, what goes wrong
when it is injured or diseased--has increased dramatically. However, we still have
much more to learn. The need for continued study of the brain is compelling: millions
of Americans are affected each year by disorders of the brain ranging from
neurogenetic diseases to degenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's, as well as
stroke, schizophrenia, autism, and impairments of speech, language, and hearing’.
Bush, 1990
- This isn’t just basic science it has practical implications.
Techniques for assessing brain anatomy;
- CAT/MRI
Techniques for assessing physiological function;
- SPECT/PET/fMRI/EEG/ERP/MEG/NIRs
Techniques for modulating brain activity;
- TMS
CAT;
- Old technique assessing structural integrity but widely used
in hospitals
- Computerized axial tomography more often called CT today
- Dense tissue (e.g., bone) appears white
- Less dense (e.g., CSF) appears black
- A series of oblique slices of the brain (9-12)
- Slices of CAT scan can show region of high density (picture 1
so, good at visualising lesion caused by stroke = Hematoma.
- Slices of a CAT scan showing regions of low density (picture
2) = Ischemia.
- CAT scan can also so water on the brain (hydrocephalus)
and that causes compression of the brain.
Advantages/disadvantages;
- Provides structural image of the brain
- Can be used in healthy and clinical participants
- Shows areas of brain abnormality (resolution 5mm)
- Relatively non-invasive
- Inexpensive
- No measure of ongoing activity
, MRI;
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Relies on magnetic fields to distort behaviour of protons
- Scanner is tuned to detect radio frequencies emitted from hydrogen atoms
- Different concentrations of hydrogen atoms in different tissue
- 3 different planes
- MRI and brain lesions
Necessary equipment;
- Big magnetic field = protons (hydrogen molecules) in body become aligned
to field.
- RF (radio frequency) coil = radio frequency pulse which knocks protons
over. As protons realign with field, they emit energy that coil receives (like
an antenna)
- Gradient coils = make it possible to encode spatial information.
- MRI produced really clear scans and so is more likely to find really small
lesions. It detects spatial resolutions of as small as 1mm.
Advantages;
- Non-invasive
- Clear structural images: Good spatial resolution (1-2mm)
- No known biological risk: Does not expose individual to X-rays
- Very good spatial resolution
Disadvantages;
- Claustrophobia
- Ferromagnetic materials / pacemakers!
- Good images hard to obtain near large cavities
- Tumours might be mistaken for cells with excess fluid
- Head placement / noisy
SPECT;
- Single photon emission computerised tomography
- Used to measure brain function
- Useful for damaged and intact brains
- Gamma emitting radioactive tracer
- SPECT measure brain’s uptake of radioactively labelled oxygen
- Sensitive to changes in blood flow
- Injection of radiopharmaceutical and scan after 30 mins
- Neural activity in related to increase in demand for blood so,
rather than a direct measurement it capitalises on the idea that
if an area is demanding more fuel then we can make the link that this area is been
more active.
Alzheimer’s Disease;
- 72 year old man with history of progressive short term memory loss
- Bilateral cortical perfusion defects involving the temporal and
parietal lobes
- Shows BLOOD FLOW DEFICITS.