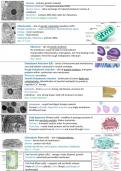
Nucleus - contains genetic material
Nuclear envelope – compartmentalizes DNA.
Nuclear pores – allow exchange of materials between nucleus &
cytoplasm
Nucleolus – contains DNA that codes for ribosomes.
Size: 6-10 um. Biggest organelle
Mitochondria – site of aerobic respiration (produces ATP)
Double membrane – Outer membrane, intermembrane space,
Cristae – inner membrane.
Matrix – fluid interior
Lipid granules, ribosomes, and own DNA.
Size: 2 -5 um
Ribosome – site of protein synthesis
No membrane, made of large & small subunit.
Found within mitochondria, chloroplasts. Are Free floating in the
cytoplasm. Form the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Size: 20nm
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – series of interconnected membranous
sacs and tubules connected to nuclear envelope.
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum – site of protein synthesis, transports
proteins within, synthesises new membranes.
Ribosomes on surface
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum - Synthesises & stores lipids and
carbohydrates, detoxification of harmful metabolic by-products,
regulates Ca2+ storage.
Centriole – forms a spindle during cell division, structure for
microtubules.
Cylindrical – very strong shape, hold cell structures in place.
Size: 0.25um diameter
Lysosomes – engulf and digest foreign material
Contain hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes, in a single membrane.
All different sizes
Golgi Apparatus (Animal cells) – modifies & packages proteins &
lipids into secretory vesicles. Makes lysosomes
Cis face – transport vesicles enter for processing.
Trans face – newly made proteins exit in small vesicles.
Transport vesicles fuse to cisternae and travel through lumen.
Chloroplasts (Plant cells) – site of photosynthesis.
Grana – dense stack of membranes
Stroma – protein rich fluid
Double membrane, starch grains, ribosomes, thylakoids.
Size: 5 – 10 um
Sap Vacuole (plant cells) – storage, waste disposal, growth
Tonoplast- selectively permeable membrane
Cell Wall (Plant cells) – supports cell and limits volume.
Made of cellulose (plants), chitin (fungi), peptidoglycan
(prokaryotic)
Nuclear envelope – compartmentalizes DNA.
Nuclear pores – allow exchange of materials between nucleus &
cytoplasm
Nucleolus – contains DNA that codes for ribosomes.
Size: 6-10 um. Biggest organelle
Mitochondria – site of aerobic respiration (produces ATP)
Double membrane – Outer membrane, intermembrane space,
Cristae – inner membrane.
Matrix – fluid interior
Lipid granules, ribosomes, and own DNA.
Size: 2 -5 um
Ribosome – site of protein synthesis
No membrane, made of large & small subunit.
Found within mitochondria, chloroplasts. Are Free floating in the
cytoplasm. Form the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Size: 20nm
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – series of interconnected membranous
sacs and tubules connected to nuclear envelope.
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum – site of protein synthesis, transports
proteins within, synthesises new membranes.
Ribosomes on surface
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum - Synthesises & stores lipids and
carbohydrates, detoxification of harmful metabolic by-products,
regulates Ca2+ storage.
Centriole – forms a spindle during cell division, structure for
microtubules.
Cylindrical – very strong shape, hold cell structures in place.
Size: 0.25um diameter
Lysosomes – engulf and digest foreign material
Contain hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes, in a single membrane.
All different sizes
Golgi Apparatus (Animal cells) – modifies & packages proteins &
lipids into secretory vesicles. Makes lysosomes
Cis face – transport vesicles enter for processing.
Trans face – newly made proteins exit in small vesicles.
Transport vesicles fuse to cisternae and travel through lumen.
Chloroplasts (Plant cells) – site of photosynthesis.
Grana – dense stack of membranes
Stroma – protein rich fluid
Double membrane, starch grains, ribosomes, thylakoids.
Size: 5 – 10 um
Sap Vacuole (plant cells) – storage, waste disposal, growth
Tonoplast- selectively permeable membrane
Cell Wall (Plant cells) – supports cell and limits volume.
Made of cellulose (plants), chitin (fungi), peptidoglycan
(prokaryotic)