DNA Sequencing
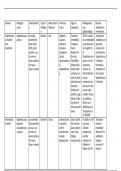
Sanger’s Method
Modified nucleotides – terminator bases – prematurely stop (truncate) synthesis
Heated to 95⁰C to separate DNA strands
Cooled to 50⁰C t allow primers to anneal
Heated to 60⁰C to allow DNA polymerase to begin synthesis of complementary strand
Terminator bases are added to a mixture containing a template strand synthesising a
complementary strand and free nucleotides
Terminator bases are added at different times to truncate the DNA at different lengths
Fragments sorted in order of length by gel electrophoresis
Computer reads radioactive or fluorescent tags attached to modified nucleotides
Pyrosequencing
DNA cut into fragments – one strand from each fragment attached to a small bead
Amplified by PCR and put into wells
Free nucleotides attach – when attaching to a bead, enzymes emit a light
Lights analysed by a computer – process 400 million base pairs in 10 hours
Sanger’s Method
Modified nucleotides – terminator bases – prematurely stop (truncate) synthesis
Heated to 95⁰C to separate DNA strands
Cooled to 50⁰C t allow primers to anneal
Heated to 60⁰C to allow DNA polymerase to begin synthesis of complementary strand
Terminator bases are added to a mixture containing a template strand synthesising a
complementary strand and free nucleotides
Terminator bases are added at different times to truncate the DNA at different lengths
Fragments sorted in order of length by gel electrophoresis
Computer reads radioactive or fluorescent tags attached to modified nucleotides
Pyrosequencing
DNA cut into fragments – one strand from each fragment attached to a small bead
Amplified by PCR and put into wells
Free nucleotides attach – when attaching to a bead, enzymes emit a light
Lights analysed by a computer – process 400 million base pairs in 10 hours