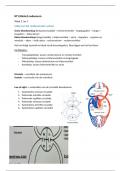
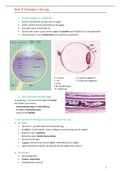
Chapter 2: Biomolecules
Sunday, 24 April 2022 9:03 PM
TESTING FOR BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES:
MOLECULE TEST
Reducing Benedict's test: reducing sugars reduce the distinctive blue copper sulfate to insoluble brick-red coppe
Sugars oxide (brick-red ppt) Blue -> Green -> Yellow -> Orange-red -> brick-red (positive test)
Non-reducing • Heat the solution with hydrochloric acid
sugars • Neutralise the test solution by adding an alkali
• Add benedict's reagent and heat as before and look for colour change
(If solution goes red, non-reducing sugar is present, if both reducing and non-reducing sugars are
present precipitate will be heavier than previous one, no colour change - no sugar present)
Starch Iodine test: Add few drops of iodine in potassium iodide solution
Colour changes from orange/brown to blue-black
Lipids Emulsion test: Add ethanol to the sample to be tested, shake to mix and then add the mixture to a tes
tube of water
If lipids are present, a milky emulsion will form (the solution appears ‘cloudy’); the more lipid present,
the more obvious the milky colour of the solution
Proteins Biuret test:
Treat the sample with sodium or potassium hydroxide
Add few drops of copper (II) sulfate which is blue in colour
A purple/lilac colour indicates protein is present
CONDENSATION REACTION:
A chemical reaction involving the joining together of two molecules by removal of water molecules
HYDROLYSIS REACTION:
Breaking of a chemical bond by addition of water molecule
CARBOHYDRATES:
• All molecules contain C, H and O
• General formula:
• Classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
• Monosaccharides - single sugar monomer
- used as source of energy in respiration (glucose)
- building blocks in polymers
• Disaccharides - two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds
- Maltose (α-glucose + α-glucose) , Sucrose (α-glucose + fructose) , Lactose (β-galactose + α-glucose
- sugar found in germinating seeds (maltose)
- mammal milk sugar (lactose)
- sugar stored in sugar-cane (sucrose)
• Polysaccharides - Many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds
- Cellulose (β-glucose) , starch (α-glucose) , glycogen (α-glucose)
AS BIOLOGY NOTES Page 1
, - Cellulose (β-glucose) , starch (α-glucose) , glycogen (α-glucose)
- energy storage (starch in plants and glycogen in animals)
• Two forms of glucose (C6H12O6) : α-glucose (OH below the ring - DDUD) and β-glucose (OH above the ring - UDU
• Reducing sugars can donate electrons (undergo oxidation). Examples, glucose, fructose and maltose
• Non-reducing sugars cannot donate electrons (undergo oxidation). Examples, sucrose
• 1,6 glycosidic bonds give branches to structure
• Starch and glycogen (storage polysaccharides):
Compact and insoluble
STARCH: - Storage polysaccharides in plants
- Made of amylose (straight-chain with 1,4 glycosidic bonds between α-glucose molecules) and
amylopectin (branched structure with 1,4 + 1,6 glycosidic bonds)
GLYCOGEN: - Storage polysaccharide in animals and fungi
- More branched than starch (more 1,6 linkages) making it more compact
CELLULOSE: - Cellulose is a polysaccharide
AS BIOLOGY NOTES Page 2
Sunday, 24 April 2022 9:03 PM
TESTING FOR BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES:
MOLECULE TEST
Reducing Benedict's test: reducing sugars reduce the distinctive blue copper sulfate to insoluble brick-red coppe
Sugars oxide (brick-red ppt) Blue -> Green -> Yellow -> Orange-red -> brick-red (positive test)
Non-reducing • Heat the solution with hydrochloric acid
sugars • Neutralise the test solution by adding an alkali
• Add benedict's reagent and heat as before and look for colour change
(If solution goes red, non-reducing sugar is present, if both reducing and non-reducing sugars are
present precipitate will be heavier than previous one, no colour change - no sugar present)
Starch Iodine test: Add few drops of iodine in potassium iodide solution
Colour changes from orange/brown to blue-black
Lipids Emulsion test: Add ethanol to the sample to be tested, shake to mix and then add the mixture to a tes
tube of water
If lipids are present, a milky emulsion will form (the solution appears ‘cloudy’); the more lipid present,
the more obvious the milky colour of the solution
Proteins Biuret test:
Treat the sample with sodium or potassium hydroxide
Add few drops of copper (II) sulfate which is blue in colour
A purple/lilac colour indicates protein is present
CONDENSATION REACTION:
A chemical reaction involving the joining together of two molecules by removal of water molecules
HYDROLYSIS REACTION:
Breaking of a chemical bond by addition of water molecule
CARBOHYDRATES:
• All molecules contain C, H and O
• General formula:
• Classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
• Monosaccharides - single sugar monomer
- used as source of energy in respiration (glucose)
- building blocks in polymers
• Disaccharides - two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds
- Maltose (α-glucose + α-glucose) , Sucrose (α-glucose + fructose) , Lactose (β-galactose + α-glucose
- sugar found in germinating seeds (maltose)
- mammal milk sugar (lactose)
- sugar stored in sugar-cane (sucrose)
• Polysaccharides - Many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds
- Cellulose (β-glucose) , starch (α-glucose) , glycogen (α-glucose)
AS BIOLOGY NOTES Page 1
, - Cellulose (β-glucose) , starch (α-glucose) , glycogen (α-glucose)
- energy storage (starch in plants and glycogen in animals)
• Two forms of glucose (C6H12O6) : α-glucose (OH below the ring - DDUD) and β-glucose (OH above the ring - UDU
• Reducing sugars can donate electrons (undergo oxidation). Examples, glucose, fructose and maltose
• Non-reducing sugars cannot donate electrons (undergo oxidation). Examples, sucrose
• 1,6 glycosidic bonds give branches to structure
• Starch and glycogen (storage polysaccharides):
Compact and insoluble
STARCH: - Storage polysaccharides in plants
- Made of amylose (straight-chain with 1,4 glycosidic bonds between α-glucose molecules) and
amylopectin (branched structure with 1,4 + 1,6 glycosidic bonds)
GLYCOGEN: - Storage polysaccharide in animals and fungi
- More branched than starch (more 1,6 linkages) making it more compact
CELLULOSE: - Cellulose is a polysaccharide
AS BIOLOGY NOTES Page 2