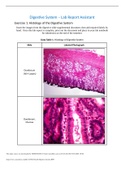
Rectal (PR) Examination
Rectal examinations are performed for several clinical reasons (altered bowel habit,
rectal bleeding and on patients with urinary symptoms).
In an OSCE station you will perform this examination on a mannequin, however you
should pretend that this is a real patient and talk to it as such.
Steps:
1. Wash your hands, introduce yourself to the patient and check their identity
before proceeding. Explain what you would like to do and obtain consent.
This is an uncomfortable procedure so you should warn the patient. As the
patient should remove all clothing below the waist, a chaperone should be
offered to the patient.
2. Ensure you have all the necessary equipment for the examination:
Gloves
Lubricant
Tissues
3. Positioning of the patient is very important. Ask them to lie on their left hand
side with their knees drawn up towards their chest.
4. Having washed your hands and put on your gloves, separate the buttocks and
inspect the area around the anus. Look for any abnormalities including skin
tags, haemorrhoids and fissures.
5. After inspecting, lubricate your right index finger.
6. Tell the patient you are about to start the examination. Place your finger on
the anus so that it’s pointing anteriorly and apply pressure to the midline of the
anus.
7. Maintain the pressure so that your finger enters the rectum. Initially you need
to assess anal tone by asking the patient to squeeze your finger.
8. Next, systematically examine the rectum. This is done by sweeping the finger
both clockwise and anti-clockwise around the circumference. You should be
feeling for any abnormalities such as impacted faeces, anal masses or ulcers.
9. In the male, one of the main reasons for performing a rectal examination is to
assess the prostate gland. This lies anteriorly and should be always be
checked. You should check the size, consistency and presence of the midline
groove.
Rectal examinations are performed for several clinical reasons (altered bowel habit,
rectal bleeding and on patients with urinary symptoms).
In an OSCE station you will perform this examination on a mannequin, however you
should pretend that this is a real patient and talk to it as such.
Steps:
1. Wash your hands, introduce yourself to the patient and check their identity
before proceeding. Explain what you would like to do and obtain consent.
This is an uncomfortable procedure so you should warn the patient. As the
patient should remove all clothing below the waist, a chaperone should be
offered to the patient.
2. Ensure you have all the necessary equipment for the examination:
Gloves
Lubricant
Tissues
3. Positioning of the patient is very important. Ask them to lie on their left hand
side with their knees drawn up towards their chest.
4. Having washed your hands and put on your gloves, separate the buttocks and
inspect the area around the anus. Look for any abnormalities including skin
tags, haemorrhoids and fissures.
5. After inspecting, lubricate your right index finger.
6. Tell the patient you are about to start the examination. Place your finger on
the anus so that it’s pointing anteriorly and apply pressure to the midline of the
anus.
7. Maintain the pressure so that your finger enters the rectum. Initially you need
to assess anal tone by asking the patient to squeeze your finger.
8. Next, systematically examine the rectum. This is done by sweeping the finger
both clockwise and anti-clockwise around the circumference. You should be
feeling for any abnormalities such as impacted faeces, anal masses or ulcers.
9. In the male, one of the main reasons for performing a rectal examination is to
assess the prostate gland. This lies anteriorly and should be always be
checked. You should check the size, consistency and presence of the midline
groove.