Antimicrobials – Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
Nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors: inhibition of base formation and blocking of DNA
coiling. Energy (ATP) required for repair also causes cell exhaustion.
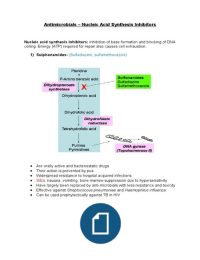
1) Sulphonamides- (Sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole)
Are orally active and bacteriostatic drugs
Their action is prevented by pus
Widespread resistance to hospital acquired infections
S/Es: nausea, vomiting, bone marrow suppression due to hypersensitivity
Have largely been replaced by anti-microbials with less resistance and toxicity
Effective against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenza
Can be used prophylactically against TB in HIV
Nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors: inhibition of base formation and blocking of DNA
coiling. Energy (ATP) required for repair also causes cell exhaustion.
1) Sulphonamides- (Sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole)
Are orally active and bacteriostatic drugs
Their action is prevented by pus
Widespread resistance to hospital acquired infections
S/Es: nausea, vomiting, bone marrow suppression due to hypersensitivity
Have largely been replaced by anti-microbials with less resistance and toxicity
Effective against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenza
Can be used prophylactically against TB in HIV