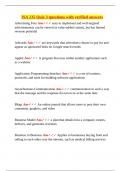
Let us consider a current element of length dL carrying current I through it. There is a point P at
distance r from current element and ɵ is the angle between dL and r.
Biot-Savart Law:
The Biot-Savart law is used to determine magnetic field(dB) at a given point, due to a current
element (current carrying conductor) and states that, magnetic field at a point due to a current
element is;
(i) directly proportional to the amount of current(I) through conductor wire, i.e.
dB ∝ I --------------(i)
(ii) directly proportional to the length(dL) of the current element, i.e
dB ∝ dL ------------(ii)
(iii) inversely proportional to square of the distance(r) of reference point from current
element, i.e.
dB ∝ 1/r2 -----------(iii)
(iv) directly proportional to the angle(ɵ) between current element(dL) and position
vector(r), i.e.
dB ∝ sinɵ ------------(iv)
Combining all above equations we get,
dB ∝ I dL sinɵ/r2
or dB = k I dL sinɵ/r2
(Here k is proportionality constant and in S.I. unit its value is [µo/4π] = 10-7 T m A-1).
Thus finally we get,
dB = (µo/4π ) (I dL sinɵ)/r2 -------------(v)
This equation is the mathematical form of Biot-Savart law.
Total magnetic field due to the whole wire cab be determined by integrating equation (v) over
the length of wire.
In vector form Biot-Savart law(v) can be written as;