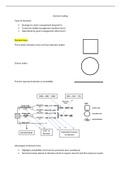
Types of decisions:
Strategic by senior management (long-term)
Tactical by middle management (medium-term)
Operational by junior management (short-term)
Decision trees:
This is where decisions come out from (decision nodes)
Chance nodes
This line represents decision or probability
1000 + 480 = 1480 300 + 450 = 750
COST of Expected revenue
DO NOTHING decision of decision
Advantages of decision trees:
Highlights probabilities that had not previously been considered.
Numerical values placed on decisions tends to require research and thus improves results.
, The methods take account of the risks involved in decisions and makes the decision-maker
aware of them.
Disadvantages of decision trees:
Probabilities are often estimating hence may be inaccurate/incorrect.
Don’t take into account non-numerical factors e.g., legal constraints.
Time lag may make numerical data out of date.
Process can be quite time-consuming.
Diagrams can become unmanageable for complex decisions.
Critical path analysis
Critical path analysis is a planning technique that identifies the individual tasks of a project, places
them in the correct sequence and allows for identification of the critical path.
The diagrams:
Arrows show activities
Must go left to right
Begin and end with a node
Length is not important
Nodes
Represents the start and end of an activity
Rules:
All diagrams start and end with a node.
There is no limit to the number of activities that link to a single node.
Line must not cross.
Calculating EST:
Work from left to right.
EST is 0 for first node.