15.11.19
L6 – Pancreatic hormones
Keywords:
Hypertrophy (cellular thickening), endocrine,
exocrine, lipogenesis (formation of lipids to be
stored as fat when blood glucose is high), lipolysis
(degradation of lipids when blood glucose is low to
form FAs), fed state (insulin dominates), fasted
state (glucagon dominates), cachexia (wasting
caused by chronic illness), hypertrophy (increase
in cell size), atherosclerotic vascular disease (build
up of plaque in arteries/veins leading to heart
failure/stroke), retinopathy (eye complications),
Heterotetramer (protein w/4 non-covalently bonded unidentical subunits)
Lecture:
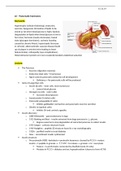
The Pancreas
o Exocrine (digestive enzymes)
o Endocrine (islet cells → hormones)
o Ngn3 controls pancreatic endocrine cell development
Deficiency = No pancreatic cells will be produced
Islets of Langerhan cells
o Insulin (β cells – inner cells, most numerous)
Lowers blood glucose
o Glucagon (α cells – outer cells)
Increases blood glucose
o Somatostatin (δ (delta) cells)
o Pancreatic polypeptide (F cells)
Inhibits gallbladder contraction and pancreatic exocrine secretion
o Ghrelin (ε (epsilon) cells)
Inhibits GH and controls appetite
Insulin discovery
o 1889 Minkowski – pancreatectomy in dogs
o 1921 Banting and Best – insulin extracted from dogs pancreas to ↓ glucose
Regress exocrine to stop degradation of extracted pancreas to collect insulin
o 1955 Sanger – primary structure found
o 1969 Hodgkins – peptide 3D structure found in x-ray crystallography
o 1920s – purified insulin to treat diabetes
o Now – recombinant insulin synthesized
Insulin structure
o Pre-proinsulin (RER) -hydrolysis→ proinsulin hexamers -cleaved by PC1/3-> mature
insulin + C peptide in granule → ↑↑ATP = Ca release → granule + Ca = exocytosis
Mature = A and B chains connected by disulfide bonds (51 AAs)
Mutates in PC1/3 = diabetes and sec hypoadrenalism (cleaves to form ACTH)
, 15.11.19
o Insulin stored as proinsulin hexamers (synth in golgi) w/ 6 molecules to 1 Zn core in
β cell secretary granules
Insulin receptor
o Heterotetrametric = 2α subunits (crosslinked w/disulfide bonds on outside) and 2β
(intermembrane protein subunit) and β changes structure when insulin binds to
extracellular α units which allows ATP to bind to intracellular β = phosphorylation to
activate tyrosine kinase domains
o Activated tyrosine kinase allows phosphorylation of other intracellular proteins and
allows ↑ uptake of glucose/transporters in CM
Action summary of insulin (main sites of action)
o Lowers blood glucose (pulsatile)
Β cells -insulin→ portal vein
First intense phase of release (mins) then less intense
o Muscle (glucose uptake via GLUT4 (transporter in muscle) to ↑ glycogen synth,
protein synth, stops protein degradation and allows AA→cell)
o Liver (↑ glycogen synth, lipogenesis and ↓ gluconeogenesis)
Removes 60% of insulin from blood (portal vein 3 folds higher in conc than
anywhere else)
o Adipose (↑ glucose transport (via GLUT4 transporter), ↑ lipogenesis (FA→
lipids/fats) and ↓ lipolysis)
GLUT-4 and the movement of glucose into cells
o GLUT-4 identifies glucose outside cell
o Glucose -glucokinase (glycolysis)→ ATP
o ATP closes K channel (cannot leave) = depo of memb
o ↑Ca2+ by opened VSGC proteins = granular insulin release via exocytosis
Insulin effects on fuels (fats, glycogen and proteins)
o Storage = ↓ levels in
serum glucose
free fatty acids
ketoacids
AA
o BBB allows glucose to pass though from ECM = needs to be ↑ reg
Carbohydrate use (and stop breakdown)
o Upreg of GLUT4 in muscles/adipose = ↑ uptake of glucose by exocytosis and fusing
membranes with the PM to attach GLUT4
Reverse endocytosis if down regulated required
Reg of insulin on liver cells
Reg of insulin secretion
o Nutrients (glucose/AAs)
o Glucose – GLUT 2 diffuse→ β cells
o Glucose -glucokinase→ produce ATP
o ATP + K+ channel inhibited = accumulation of K+ = depolarised cell
o Voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels open and it flows in and insulin released from storage
granules (glucose stim uptake of insulin)
o Sulphonyl-urea receptor activated also means that the cell depolarises
Neural regs of insulin
L6 – Pancreatic hormones
Keywords:
Hypertrophy (cellular thickening), endocrine,
exocrine, lipogenesis (formation of lipids to be
stored as fat when blood glucose is high), lipolysis
(degradation of lipids when blood glucose is low to
form FAs), fed state (insulin dominates), fasted
state (glucagon dominates), cachexia (wasting
caused by chronic illness), hypertrophy (increase
in cell size), atherosclerotic vascular disease (build
up of plaque in arteries/veins leading to heart
failure/stroke), retinopathy (eye complications),
Heterotetramer (protein w/4 non-covalently bonded unidentical subunits)
Lecture:
The Pancreas
o Exocrine (digestive enzymes)
o Endocrine (islet cells → hormones)
o Ngn3 controls pancreatic endocrine cell development
Deficiency = No pancreatic cells will be produced
Islets of Langerhan cells
o Insulin (β cells – inner cells, most numerous)
Lowers blood glucose
o Glucagon (α cells – outer cells)
Increases blood glucose
o Somatostatin (δ (delta) cells)
o Pancreatic polypeptide (F cells)
Inhibits gallbladder contraction and pancreatic exocrine secretion
o Ghrelin (ε (epsilon) cells)
Inhibits GH and controls appetite
Insulin discovery
o 1889 Minkowski – pancreatectomy in dogs
o 1921 Banting and Best – insulin extracted from dogs pancreas to ↓ glucose
Regress exocrine to stop degradation of extracted pancreas to collect insulin
o 1955 Sanger – primary structure found
o 1969 Hodgkins – peptide 3D structure found in x-ray crystallography
o 1920s – purified insulin to treat diabetes
o Now – recombinant insulin synthesized
Insulin structure
o Pre-proinsulin (RER) -hydrolysis→ proinsulin hexamers -cleaved by PC1/3-> mature
insulin + C peptide in granule → ↑↑ATP = Ca release → granule + Ca = exocytosis
Mature = A and B chains connected by disulfide bonds (51 AAs)
Mutates in PC1/3 = diabetes and sec hypoadrenalism (cleaves to form ACTH)
, 15.11.19
o Insulin stored as proinsulin hexamers (synth in golgi) w/ 6 molecules to 1 Zn core in
β cell secretary granules
Insulin receptor
o Heterotetrametric = 2α subunits (crosslinked w/disulfide bonds on outside) and 2β
(intermembrane protein subunit) and β changes structure when insulin binds to
extracellular α units which allows ATP to bind to intracellular β = phosphorylation to
activate tyrosine kinase domains
o Activated tyrosine kinase allows phosphorylation of other intracellular proteins and
allows ↑ uptake of glucose/transporters in CM
Action summary of insulin (main sites of action)
o Lowers blood glucose (pulsatile)
Β cells -insulin→ portal vein
First intense phase of release (mins) then less intense
o Muscle (glucose uptake via GLUT4 (transporter in muscle) to ↑ glycogen synth,
protein synth, stops protein degradation and allows AA→cell)
o Liver (↑ glycogen synth, lipogenesis and ↓ gluconeogenesis)
Removes 60% of insulin from blood (portal vein 3 folds higher in conc than
anywhere else)
o Adipose (↑ glucose transport (via GLUT4 transporter), ↑ lipogenesis (FA→
lipids/fats) and ↓ lipolysis)
GLUT-4 and the movement of glucose into cells
o GLUT-4 identifies glucose outside cell
o Glucose -glucokinase (glycolysis)→ ATP
o ATP closes K channel (cannot leave) = depo of memb
o ↑Ca2+ by opened VSGC proteins = granular insulin release via exocytosis
Insulin effects on fuels (fats, glycogen and proteins)
o Storage = ↓ levels in
serum glucose
free fatty acids
ketoacids
AA
o BBB allows glucose to pass though from ECM = needs to be ↑ reg
Carbohydrate use (and stop breakdown)
o Upreg of GLUT4 in muscles/adipose = ↑ uptake of glucose by exocytosis and fusing
membranes with the PM to attach GLUT4
Reverse endocytosis if down regulated required
Reg of insulin on liver cells
Reg of insulin secretion
o Nutrients (glucose/AAs)
o Glucose – GLUT 2 diffuse→ β cells
o Glucose -glucokinase→ produce ATP
o ATP + K+ channel inhibited = accumulation of K+ = depolarised cell
o Voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels open and it flows in and insulin released from storage
granules (glucose stim uptake of insulin)
o Sulphonyl-urea receptor activated also means that the cell depolarises
Neural regs of insulin