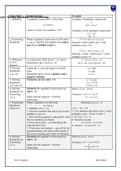
Topic/Skill
Topic: Solving Definition/Tips
Quadratics by Factorising Example
1. Quadratic A quadratic expression is of the form Examples of quadratic expressions:
2
x
2
a x +bx+ c 2
8 x −3 x+ 7
where a , b and c are numbers, a ≠ 0 Examples of non-quadratic expressions:
3 2
2 x −5 x
9 x−1
2. Factorising When a quadratic expression is in the form 2
x + 7 x +10=(x +5)( x +2)
Quadratics 2
x + bx+ c find the two numbers that add to (because 5 and 2 add to give 7 and
give b and multiply to give c. multiply to give 10)
x 2+ 2 x−8=(x+ 4)(x−2)
(because +4 and -2 add to give +2 and
multiply to give -8)
3. Difference An expression of the form a 2−b2 can be x 2−25=(x +5)( x−5)
of Two factorised to give (a+ b)(a−b) 16 x 2−81=(4 x+ 9)( 4 x−9)
Squares
4. Solving Isolate the x 2 term and square root both 2
2 x =98
Quadratics sides. 2
x =49
2
(a x =b) Remember there will be a positive and a x=± 7
negative solution.
5. Solving Factorise and then solve = 0. 2
x −3 x=0
Quadratics x ( x−3 )=0
2
(a x +bx=0) x=0∨x=3
6. Solving Factorise the quadratic in the usual way. 2
Solve x + 3 x −10=0
Quadratics by Solve = 0
Factorising Factorise: ( x +5 ) ( x−2 )=0
( a=1 ) Make sure the equation = 0 before x=−5∨x=2
factorising.
7. Factorising When a quadratic is in the form Factorise 6 x 2+ 5 x−4
Quadratics a x 2 +bx+ c
when a ≠ 1 1. Multiply a by c = ac 1. 6 ×−4=−24
2. Find two numbers that add to give b and 2. Two numbers that add to give +5 and
multiply to give ac. multiply to give -24 are +8 and -3
3. Re-write the quadratic, replacing bx with 3. 6 x 2+ 8 x−3 x−4
the two numbers you found. 4. Factorise in pairs:
4. Factorise in pairs – you should get the 2 x ( 3 x+ 4 )−1(3 x +4)
same bracket twice 5. Answer = (3 x+ 4)(2 x−1)
5. Write your two brackets – one will be the
repeated bracket, the other will be made of
the factors outside each of the two brackets.
8. Solving Factorise the quadratic in the usual way. Solve 2 x2 +7 x−4=0
Quadratics by Solve = 0
Factorising Factorise: ( 2 x−1 ) ( x + 4 ) =0
(a ≠ 1) Make sure the equation = 0 before 1
factorising. x= ∨x=−4
2
Mr A. Coleman Glyn School
Topic: Solving Definition/Tips
Quadratics by Factorising Example
1. Quadratic A quadratic expression is of the form Examples of quadratic expressions:
2
x
2
a x +bx+ c 2
8 x −3 x+ 7
where a , b and c are numbers, a ≠ 0 Examples of non-quadratic expressions:
3 2
2 x −5 x
9 x−1
2. Factorising When a quadratic expression is in the form 2
x + 7 x +10=(x +5)( x +2)
Quadratics 2
x + bx+ c find the two numbers that add to (because 5 and 2 add to give 7 and
give b and multiply to give c. multiply to give 10)
x 2+ 2 x−8=(x+ 4)(x−2)
(because +4 and -2 add to give +2 and
multiply to give -8)
3. Difference An expression of the form a 2−b2 can be x 2−25=(x +5)( x−5)
of Two factorised to give (a+ b)(a−b) 16 x 2−81=(4 x+ 9)( 4 x−9)
Squares
4. Solving Isolate the x 2 term and square root both 2
2 x =98
Quadratics sides. 2
x =49
2
(a x =b) Remember there will be a positive and a x=± 7
negative solution.
5. Solving Factorise and then solve = 0. 2
x −3 x=0
Quadratics x ( x−3 )=0
2
(a x +bx=0) x=0∨x=3
6. Solving Factorise the quadratic in the usual way. 2
Solve x + 3 x −10=0
Quadratics by Solve = 0
Factorising Factorise: ( x +5 ) ( x−2 )=0
( a=1 ) Make sure the equation = 0 before x=−5∨x=2
factorising.
7. Factorising When a quadratic is in the form Factorise 6 x 2+ 5 x−4
Quadratics a x 2 +bx+ c
when a ≠ 1 1. Multiply a by c = ac 1. 6 ×−4=−24
2. Find two numbers that add to give b and 2. Two numbers that add to give +5 and
multiply to give ac. multiply to give -24 are +8 and -3
3. Re-write the quadratic, replacing bx with 3. 6 x 2+ 8 x−3 x−4
the two numbers you found. 4. Factorise in pairs:
4. Factorise in pairs – you should get the 2 x ( 3 x+ 4 )−1(3 x +4)
same bracket twice 5. Answer = (3 x+ 4)(2 x−1)
5. Write your two brackets – one will be the
repeated bracket, the other will be made of
the factors outside each of the two brackets.
8. Solving Factorise the quadratic in the usual way. Solve 2 x2 +7 x−4=0
Quadratics by Solve = 0
Factorising Factorise: ( 2 x−1 ) ( x + 4 ) =0
(a ≠ 1) Make sure the equation = 0 before 1
factorising. x= ∨x=−4
2
Mr A. Coleman Glyn School