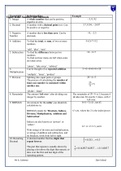
Topic/Skill
Topic: Definition/Tips
Basic Number and Decimals Example
1. Integer A whole number that can be positive, −3 , 0 , 92
negative or zero.
2. Decimal A number with a decimal point in it. Can 3.7 , 0.94 ,−24.07
be positive or negative.
3. Negative A number that is less than zero. Can be −8 ,−2.5
Number decimals.
4. Addition To find the total, or sum, of two or more 3+2+7=12
numbers.
‘add’, ‘plus’, ‘sum’
5. Subtraction To find the difference between two 10−3=7
numbers.
To find out how many are left when some
are taken away.
‘minus’, ‘take away’, ‘subtract’
6. Can be thought of as repeated addition. 3 ×6=6+6 +6=18
Multiplication
‘multiply’, ‘times’, ‘product’
7. Division Splitting into equal parts or groups. 20 ÷ 4=5
The process of calculating the number of
times one number is contained within 20
=5
another one. 4
‘divide’, ‘share’
8. Remainder The amount ‘left over’ after dividing one The remainder of 20 ÷ 6 is 2, because 6
integer by another. divides into 20 exactly 3 times, with 2
left over.
9. BIDMAS An acronym for the order you should do 6+3 × 5=21 , not 45
calculations in.
2
BIDMAS stands for ‘Brackets, Indices, 5 =25 , where the 2 is the index/power.
Division, Multiplication, Addition and
Subtraction’.
Indices are also known as ‘powers’ or
‘orders’.
12 ÷ 4 ÷ 2=1.5 , not 6
With strings of division and multiplication,
or strings of addition and subtraction, and
no brackets, work from left to right.
10. Recurring A decimal number that has digits that 1
=0.333 …=0. 3̇
Decimal repeat forever. 3
The part that repeats is usually shown by 1
=0.142857142857 …=0. 1̇ 4285 7̇
placing a dot above the digit that repeats, or 7
dots over the first and last digit of the
repeating pattern.
Mr A. Coleman Glyn School
Topic: Definition/Tips
Basic Number and Decimals Example
1. Integer A whole number that can be positive, −3 , 0 , 92
negative or zero.
2. Decimal A number with a decimal point in it. Can 3.7 , 0.94 ,−24.07
be positive or negative.
3. Negative A number that is less than zero. Can be −8 ,−2.5
Number decimals.
4. Addition To find the total, or sum, of two or more 3+2+7=12
numbers.
‘add’, ‘plus’, ‘sum’
5. Subtraction To find the difference between two 10−3=7
numbers.
To find out how many are left when some
are taken away.
‘minus’, ‘take away’, ‘subtract’
6. Can be thought of as repeated addition. 3 ×6=6+6 +6=18
Multiplication
‘multiply’, ‘times’, ‘product’
7. Division Splitting into equal parts or groups. 20 ÷ 4=5
The process of calculating the number of
times one number is contained within 20
=5
another one. 4
‘divide’, ‘share’
8. Remainder The amount ‘left over’ after dividing one The remainder of 20 ÷ 6 is 2, because 6
integer by another. divides into 20 exactly 3 times, with 2
left over.
9. BIDMAS An acronym for the order you should do 6+3 × 5=21 , not 45
calculations in.
2
BIDMAS stands for ‘Brackets, Indices, 5 =25 , where the 2 is the index/power.
Division, Multiplication, Addition and
Subtraction’.
Indices are also known as ‘powers’ or
‘orders’.
12 ÷ 4 ÷ 2=1.5 , not 6
With strings of division and multiplication,
or strings of addition and subtraction, and
no brackets, work from left to right.
10. Recurring A decimal number that has digits that 1
=0.333 …=0. 3̇
Decimal repeat forever. 3
The part that repeats is usually shown by 1
=0.142857142857 …=0. 1̇ 4285 7̇
placing a dot above the digit that repeats, or 7
dots over the first and last digit of the
repeating pattern.
Mr A. Coleman Glyn School