Oxidation - gaining of oxygen or the loss of electrons
Reduction - loss of oxygen or the gaining of electrons
Redox - abbreviation of oxidation reduction. Movement of electrons between atoms
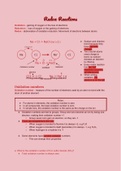
Na + Cl -> NaCl (Na+) (Cl-) ● Sodium and chlorine
bond because they
have opposite
charges
● Two neutral atoms
need charge to
bond, so sodium
0 donates an electron
0 +1 -1 to chlorine
Na + Cl -> NaCl ● Every redox reaction
Oxidation number oxidised reduced has two half
reactions occurring
electron simultaneously
● When writing
Cl + e- -> Cl- Na -> Na+ + e- oxidation, the
Writing reduction Writing oxidation
half reactions
electron is on the left
Oxidation numbers
Oxidation number - measure of the number of electrons used by an atom to bond with the
atom of another element
Rules:
● For atoms in elements, the oxidation number is zero
● In all compounds, the total oxidation number is zero
● In simple ions, the oxidation number is the same as the charge on the ion
● Oxidation numbers are tied to groups. Group one ions become an ion by losing one
electron, making their oxidation number +1
○ Group seven ions gain an electron, so they are -1
● There are exceptions to the rule:
○ When oxygen is bonded to fluorine it is always +2, e.g F2O
○ When oxygen is bonded to itself (peroxides) it is always -1, e.g H2O2
○ When hydrogen is a hydride it is -1
● Some elements have variable oxidation numbers
○ This can change their properties
e: What is the oxidation number of S in sulfur dioxide (SO2)?
● Total oxidation number is always zero