Department of Mathematics Elementary Graph Theory Lecture 10
Degree Sequence and Degree Set
Degree sequence
A sequence d1 , d 2 , , d p of non-negative integer is called a degree
sequence of a graph G, if the vertices of G labeled as: v1 , v2 , , v p , such
that deg(vi ) di , i , i 1, 2,..., p .
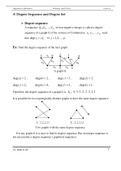
Ex: Find the degree sequence of the next graph:
z f
a b k
c d h
A graph G
deg(a ) 2 , deg(b) 2 , deg(c) 3 , deg(d ) 3 ,
deg( z ) 2 , deg(h) 4 , deg( f ) 1, deg(k ) 1 ,
Therefore, the degree sequence of a graph G is SG : 4, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1
It is possible for two topologically distinct graphs to have the same degree sequence.
Two graphs with the same degree sequence
For any graph G it is easy to find its degree sequence. But an integer sequence is
not necessarily a degree sequence ( graphical sequence).
Dr. Didar A. Ali 1
, Department of Mathematics Elementary Graph Theory Lecture 10
Theorem : The following are necessary condition for a non-negative integer
sequence S : d1 , d 2 , , d p to be graphical:
p
1. The sum of the di is even number ( di even number ).
i 1
2. di p 1 , for 1 i p .
3. At least two number in the sequence S are equal.
Ex: The sequence S : 3,3,3,1 satisfies all the above necessary condition, but it is
not graphical sequence.
The most important question is: Can we determine when a sequence is graphical?
The answer to our question was provided by Theorem of Haval-Hakimi.
Theorem : ( Haval-Hakimi)
A sequence S : d1 , d 2 , , dp of non-negative integers with
n 1 d1 d 2 d p 0 with p 2, d1 1 is a graphical sequence if and only if the
modified sequence S d 2 1, d3 1, , d d1 1 , d d1 2 , , d n is graphical.
Algorithm: To test a sequence S to be Graphical Sequence. Apply the following
algorithm
1. If there exists an integer d in S such that d p 1 , then halt and answer no.
2. If the sequence is all zeros, then halt and answer yes.
3. If the sequence contains a negative number, then halt and answer no.
4. Reorder the sequence (if necessary) so that it is non-increasing.
Dr. Didar A. Ali 2
Degree Sequence and Degree Set
Degree sequence
A sequence d1 , d 2 , , d p of non-negative integer is called a degree
sequence of a graph G, if the vertices of G labeled as: v1 , v2 , , v p , such
that deg(vi ) di , i , i 1, 2,..., p .
Ex: Find the degree sequence of the next graph:
z f
a b k
c d h
A graph G
deg(a ) 2 , deg(b) 2 , deg(c) 3 , deg(d ) 3 ,
deg( z ) 2 , deg(h) 4 , deg( f ) 1, deg(k ) 1 ,
Therefore, the degree sequence of a graph G is SG : 4, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1
It is possible for two topologically distinct graphs to have the same degree sequence.
Two graphs with the same degree sequence
For any graph G it is easy to find its degree sequence. But an integer sequence is
not necessarily a degree sequence ( graphical sequence).
Dr. Didar A. Ali 1
, Department of Mathematics Elementary Graph Theory Lecture 10
Theorem : The following are necessary condition for a non-negative integer
sequence S : d1 , d 2 , , d p to be graphical:
p
1. The sum of the di is even number ( di even number ).
i 1
2. di p 1 , for 1 i p .
3. At least two number in the sequence S are equal.
Ex: The sequence S : 3,3,3,1 satisfies all the above necessary condition, but it is
not graphical sequence.
The most important question is: Can we determine when a sequence is graphical?
The answer to our question was provided by Theorem of Haval-Hakimi.
Theorem : ( Haval-Hakimi)
A sequence S : d1 , d 2 , , dp of non-negative integers with
n 1 d1 d 2 d p 0 with p 2, d1 1 is a graphical sequence if and only if the
modified sequence S d 2 1, d3 1, , d d1 1 , d d1 2 , , d n is graphical.
Algorithm: To test a sequence S to be Graphical Sequence. Apply the following
algorithm
1. If there exists an integer d in S such that d p 1 , then halt and answer no.
2. If the sequence is all zeros, then halt and answer yes.
3. If the sequence contains a negative number, then halt and answer no.
4. Reorder the sequence (if necessary) so that it is non-increasing.
Dr. Didar A. Ali 2