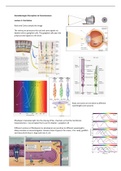
Aantekeningen Perception to Consciousness
Lecture 1: the Retina
Rods and Cones sample the image
The retina pre-processes the rod and cone signals via
bipolar cells to ganglion cells. The ganglion cells pass the
preprocessed signals to the brain
Rods and cones are sensitive to different
wavelengths (see picture)
Rhodopsin translates light into the closing of Na+ channels so that the membrane
hyperpolarizes > neural signal that is sent to bipolar > ganglion cell
Different versions of Rhodopsin (or photopsin) are sensitive to different wavelengths.
Many varieties in animal kingdom. Humans have 4 types (3 for cones, 1 for rods), goldfish
and many birds have 5, dogs and mice 3, etc.
,Retinal color blindness: absence of a particular cone type
Color blindness among humans is not uncommon. In males 8 out of 100 Caucasians, 5 out of
100 Asians, and 3 out of 100 Africans are color blind. The probability is 10 times less in
females. There are many tests to assess color blindness. One of the best known is the Ishihara
plates. People with normal color vision see an 8 here.
Color vision seems to be present for the whole visual field, yet cones are almost exclusively
confined to the central part of the visual field
(fovea). Rods are in the parafovea.
The Fovea: cup shaped, highest density photoreceptors, mainly cones; sharpest vision,
color vision
Fundoscopy reveals that light has
to pass a lot of obstacles to reach
the photo-receptors: veins,
vitreous body particles (‘bugs’)
Visualizing your retinal blood vessels with your smartphone
Close eyes gently. Hold light source to the side of your eye / head so that its
light is visible but not too strongly. Wiggle light up and down.
Age Related Macular Degeneration
• Older age, smoking, diet, genetic
• Loss of central vision, acuity loss
• Pigment epithelium (receptors) are lost due to accumulation of toxic
products
• No treatment (stem cells?)
,Light has to pass through the retinal network to reach the photoreceptors! Why this strange arrangement? The
pigment epithelium prevents light
scatter, so that sharper vision is possible (it also provides nutrients, etc)
Cat pigment epithelium is light reflective instead of absorbent:
• better low light vision (because same ray of light hits more photoreceptors)
• but unsharper image (due to scatter)
RGC fibers lying on top causes the blind spot: the place where all retinal ganglion cell fibers
pass through the eye (optic disk), and no receptors are present.
Visualizing your Blind Spot
- Close the left eye
- Look at your left finger
- Wiggle the right
Glaucoma
• Increase of pressure inside the eye
• Narrow angle or open angle types / acute, chronic
• Damage of nerve fibers of the RGC’s: optic nerve
• Loss of peripheral vision first (but may vary)
• Treatment: eyedrops, surgery (but lost RGC’s are lost)
The retina pre-processes the rod and cone signals
via bipolar cells to ganglion cells
The ganglion cells pass the preprocessed signals to the brain
, The need for data compression
→
How is the retinal information compressed?
A clue:
The photoreceptor responds to light by hyperpolarization (closing of Na+ channels), to dark by depolarization
(opening of Na+ channels): a graded potential signal
The photoreceptor signal is converted into ON and OFF signals at the bipolar cells, using different Glutamate
receptor types at the synapse between receptor and bipolar
A schematic of how the ON and OFF ganglion cells arise.
The photoreceptors of the vertebrate retina all hyperpolarize to light, yield only
graded potentials, and utilize the neurotransmitter glutamate.
The ON and OFF systems originate at the level of the bipolar cells. The receptors
make sign conserving synapses with the OFF bipolar cells and sign inverting
synapses with ON bipolar cells that have a unique neurotransmitter receptor site
(mGluR6).
Horizontal cells receive signals from widespread region of receptors. They provide
negative feedback on the receptors.
Lecture 1: the Retina
Rods and Cones sample the image
The retina pre-processes the rod and cone signals via
bipolar cells to ganglion cells. The ganglion cells pass the
preprocessed signals to the brain
Rods and cones are sensitive to different
wavelengths (see picture)
Rhodopsin translates light into the closing of Na+ channels so that the membrane
hyperpolarizes > neural signal that is sent to bipolar > ganglion cell
Different versions of Rhodopsin (or photopsin) are sensitive to different wavelengths.
Many varieties in animal kingdom. Humans have 4 types (3 for cones, 1 for rods), goldfish
and many birds have 5, dogs and mice 3, etc.
,Retinal color blindness: absence of a particular cone type
Color blindness among humans is not uncommon. In males 8 out of 100 Caucasians, 5 out of
100 Asians, and 3 out of 100 Africans are color blind. The probability is 10 times less in
females. There are many tests to assess color blindness. One of the best known is the Ishihara
plates. People with normal color vision see an 8 here.
Color vision seems to be present for the whole visual field, yet cones are almost exclusively
confined to the central part of the visual field
(fovea). Rods are in the parafovea.
The Fovea: cup shaped, highest density photoreceptors, mainly cones; sharpest vision,
color vision
Fundoscopy reveals that light has
to pass a lot of obstacles to reach
the photo-receptors: veins,
vitreous body particles (‘bugs’)
Visualizing your retinal blood vessels with your smartphone
Close eyes gently. Hold light source to the side of your eye / head so that its
light is visible but not too strongly. Wiggle light up and down.
Age Related Macular Degeneration
• Older age, smoking, diet, genetic
• Loss of central vision, acuity loss
• Pigment epithelium (receptors) are lost due to accumulation of toxic
products
• No treatment (stem cells?)
,Light has to pass through the retinal network to reach the photoreceptors! Why this strange arrangement? The
pigment epithelium prevents light
scatter, so that sharper vision is possible (it also provides nutrients, etc)
Cat pigment epithelium is light reflective instead of absorbent:
• better low light vision (because same ray of light hits more photoreceptors)
• but unsharper image (due to scatter)
RGC fibers lying on top causes the blind spot: the place where all retinal ganglion cell fibers
pass through the eye (optic disk), and no receptors are present.
Visualizing your Blind Spot
- Close the left eye
- Look at your left finger
- Wiggle the right
Glaucoma
• Increase of pressure inside the eye
• Narrow angle or open angle types / acute, chronic
• Damage of nerve fibers of the RGC’s: optic nerve
• Loss of peripheral vision first (but may vary)
• Treatment: eyedrops, surgery (but lost RGC’s are lost)
The retina pre-processes the rod and cone signals
via bipolar cells to ganglion cells
The ganglion cells pass the preprocessed signals to the brain
, The need for data compression
→
How is the retinal information compressed?
A clue:
The photoreceptor responds to light by hyperpolarization (closing of Na+ channels), to dark by depolarization
(opening of Na+ channels): a graded potential signal
The photoreceptor signal is converted into ON and OFF signals at the bipolar cells, using different Glutamate
receptor types at the synapse between receptor and bipolar
A schematic of how the ON and OFF ganglion cells arise.
The photoreceptors of the vertebrate retina all hyperpolarize to light, yield only
graded potentials, and utilize the neurotransmitter glutamate.
The ON and OFF systems originate at the level of the bipolar cells. The receptors
make sign conserving synapses with the OFF bipolar cells and sign inverting
synapses with ON bipolar cells that have a unique neurotransmitter receptor site
(mGluR6).
Horizontal cells receive signals from widespread region of receptors. They provide
negative feedback on the receptors.