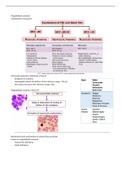
Megaloblastic anaemia
Classification of anaemia:
Macrocytic anaemia is defined as a triad of:
- Symptoms of anaemia
- Haemoglobin below the bottom of the reference range <115 g/L
- MCV above the top of the reference range >95fL
Megaloblastic anaemia: what is it?
Biochemical basis and function of vitamin B12 and folate
Causes of megaloblastic anaemia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Folate deficiency
, - Combined folate and B12 deficiency
- Abnormalities of Vitamin B12 or folate metabolism (ex. Nitrous oxide, antifolate drugs like methotrexate or
trimethoprim)
- Inherited defects of DNA synthesis or methionine synthase
- Congenital enzyme deficiencies (ex. orotic aciduria, which impairs pyrimidine synthesis)
- Acquired enzyme deficiencies (ex. Pyrimidine antagonist like cytosine arabinoside)
Vitamin B12:
- It’s synthesised by microorganisms
- We acquire vitamin B12 from the diet: mainly from meat and dairy products
- A normal diet contains a large excess of vitamin B12
- Body can store 3-4 years worth of B12, so short dietary deficiency is not problematic
Vitamin B12 absorption and transport:
1. Absorbed in the distal ileum:
a. B12 is released from protein binding in the food by pepsin in the stomach
b. B12 is bound by glycoprotein intrinsic factor (IF) which is produced by parietal cells
c. IF-B12 complex is delivered to ileum where it bind to IF receptor, cubam (cubulin
+amnionless proteins)
d. IF-B12 complex is endocytosed into the ileal cell so IF is destroyed, while B12 is absorbed and enter the plasma
2. In the plasma
a. B12 is bound by haptocorrin (80%) and transcobalamin (20%)
b. Transcobalamin delivers B12 to the cell for uptake (ex. Bone marrow, liver, etc)
Classification of anaemia:
Macrocytic anaemia is defined as a triad of:
- Symptoms of anaemia
- Haemoglobin below the bottom of the reference range <115 g/L
- MCV above the top of the reference range >95fL
Megaloblastic anaemia: what is it?
Biochemical basis and function of vitamin B12 and folate
Causes of megaloblastic anaemia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Folate deficiency
, - Combined folate and B12 deficiency
- Abnormalities of Vitamin B12 or folate metabolism (ex. Nitrous oxide, antifolate drugs like methotrexate or
trimethoprim)
- Inherited defects of DNA synthesis or methionine synthase
- Congenital enzyme deficiencies (ex. orotic aciduria, which impairs pyrimidine synthesis)
- Acquired enzyme deficiencies (ex. Pyrimidine antagonist like cytosine arabinoside)
Vitamin B12:
- It’s synthesised by microorganisms
- We acquire vitamin B12 from the diet: mainly from meat and dairy products
- A normal diet contains a large excess of vitamin B12
- Body can store 3-4 years worth of B12, so short dietary deficiency is not problematic
Vitamin B12 absorption and transport:
1. Absorbed in the distal ileum:
a. B12 is released from protein binding in the food by pepsin in the stomach
b. B12 is bound by glycoprotein intrinsic factor (IF) which is produced by parietal cells
c. IF-B12 complex is delivered to ileum where it bind to IF receptor, cubam (cubulin
+amnionless proteins)
d. IF-B12 complex is endocytosed into the ileal cell so IF is destroyed, while B12 is absorbed and enter the plasma
2. In the plasma
a. B12 is bound by haptocorrin (80%) and transcobalamin (20%)
b. Transcobalamin delivers B12 to the cell for uptake (ex. Bone marrow, liver, etc)