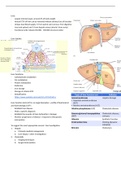
Liver:
- Largest internal organ, around 2% of body weight
- Around 75% of liver can be removed without obvious loss of function
- Unique dual blood supply: ⅔ from portal vein (venous, from digestive
tract and spleen) and ⅓ from hepatic artery (arterial, from aorta)
- Functional units: lobules (50,000 - 100,000 structural units)
Liver lobules:
Liver functions:
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Fat metabolism
- Protein metabolism
- Endocrine
- Iron storage
- Storage of vitamin B12
- Detoxification
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O71niTozP-o
Liver function tests (LFTs): no single biomarker - profile of biochemical
and haematological LFTs
- Establish liver disease
- Make a specific diagnosis
- Establish the severity of liver dysfunction / damage
- Monitor progression of disease / response to therapeutic
intervention
To suggest the most appropriate second - line investigation:
1. Hepatic
a. Primarily medical management
b. Liver biopsy / other investigations
2. Cholestatic
a. Imaging techniques
b. Surgical intervention
, Aminotransferases:
1. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
a. Present in cytosol / mitochondria of hepatocytes
b. Lacks specificity
2. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
a. Present in cytosol of hepatocytes
b. More specific for liver - activity much lower in extrahepatic tissue
Aminotransferases - indicators of hepatic damage
1. Hepatocellular damage:
a. Infective agents, autoimmune disorders, toxins
b. ALT/AST may increase by up to 100 times upper limit of reference range
c. ALT/AST useful in monitoring progress of hepatocellular damage
2. Cholestasis:
a. ALT/AST increases slightly but no more than 2-3 times upper limit of reference range
AST/ALT ratio > 2 suggestive of alcohol misuse
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): Increase in serum ALP may be caused by:
- Not specific for liver 1. Liver:
- Occurs on hepatocyte surface and microvilli of bile ducts a. Obstructions of bile ducts or ductules
1. Hepatocellular damage: b. Portal hypertensions or reduced blood flow due to left
a. ALP normal / slight raised; no more than 2 times upper limit of heart failure
reference range 2. Other causes:
2. Cholestasis: a. Paget’s disease
a. ALP is increased > 3 times upper limit of reference range b. Malignancy in the bone
b. ALP concentration useful for monitoring progress of cholestasis c. Benign transient hyperphosphatasemia (GIT infections)
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
- Also called gamma-glutamyl transferase
- GGT activity in plasma mainly attributable to the liver isoenzyme
- Raised in both hepatocellular disease and cholestasis
BUT
- Poor specificity for liver disease
- Direct relationship between GGT and alcohol
- Weight, drugs
Plasma proteins:
- Albumin is the major protein synthesised by the liver
- 12g/day: correlates with liver function, decreases serum [albumin] in chronic liver disease
- Increases plasma globulins in alcoholic cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis
Prothrombin Time (PT): the rate at which prothrombin is converted to thrombin in the presence of activated clotting
factors, calcium and thromboplastin.
- Increase is early feature of acute liver disease or vitamin K deficiency
- International normalised ratio (INR), normal: 0.8 - 1.1
- Largest internal organ, around 2% of body weight
- Around 75% of liver can be removed without obvious loss of function
- Unique dual blood supply: ⅔ from portal vein (venous, from digestive
tract and spleen) and ⅓ from hepatic artery (arterial, from aorta)
- Functional units: lobules (50,000 - 100,000 structural units)
Liver lobules:
Liver functions:
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Fat metabolism
- Protein metabolism
- Endocrine
- Iron storage
- Storage of vitamin B12
- Detoxification
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O71niTozP-o
Liver function tests (LFTs): no single biomarker - profile of biochemical
and haematological LFTs
- Establish liver disease
- Make a specific diagnosis
- Establish the severity of liver dysfunction / damage
- Monitor progression of disease / response to therapeutic
intervention
To suggest the most appropriate second - line investigation:
1. Hepatic
a. Primarily medical management
b. Liver biopsy / other investigations
2. Cholestatic
a. Imaging techniques
b. Surgical intervention
, Aminotransferases:
1. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
a. Present in cytosol / mitochondria of hepatocytes
b. Lacks specificity
2. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
a. Present in cytosol of hepatocytes
b. More specific for liver - activity much lower in extrahepatic tissue
Aminotransferases - indicators of hepatic damage
1. Hepatocellular damage:
a. Infective agents, autoimmune disorders, toxins
b. ALT/AST may increase by up to 100 times upper limit of reference range
c. ALT/AST useful in monitoring progress of hepatocellular damage
2. Cholestasis:
a. ALT/AST increases slightly but no more than 2-3 times upper limit of reference range
AST/ALT ratio > 2 suggestive of alcohol misuse
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): Increase in serum ALP may be caused by:
- Not specific for liver 1. Liver:
- Occurs on hepatocyte surface and microvilli of bile ducts a. Obstructions of bile ducts or ductules
1. Hepatocellular damage: b. Portal hypertensions or reduced blood flow due to left
a. ALP normal / slight raised; no more than 2 times upper limit of heart failure
reference range 2. Other causes:
2. Cholestasis: a. Paget’s disease
a. ALP is increased > 3 times upper limit of reference range b. Malignancy in the bone
b. ALP concentration useful for monitoring progress of cholestasis c. Benign transient hyperphosphatasemia (GIT infections)
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
- Also called gamma-glutamyl transferase
- GGT activity in plasma mainly attributable to the liver isoenzyme
- Raised in both hepatocellular disease and cholestasis
BUT
- Poor specificity for liver disease
- Direct relationship between GGT and alcohol
- Weight, drugs
Plasma proteins:
- Albumin is the major protein synthesised by the liver
- 12g/day: correlates with liver function, decreases serum [albumin] in chronic liver disease
- Increases plasma globulins in alcoholic cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis
Prothrombin Time (PT): the rate at which prothrombin is converted to thrombin in the presence of activated clotting
factors, calcium and thromboplastin.
- Increase is early feature of acute liver disease or vitamin K deficiency
- International normalised ratio (INR), normal: 0.8 - 1.1